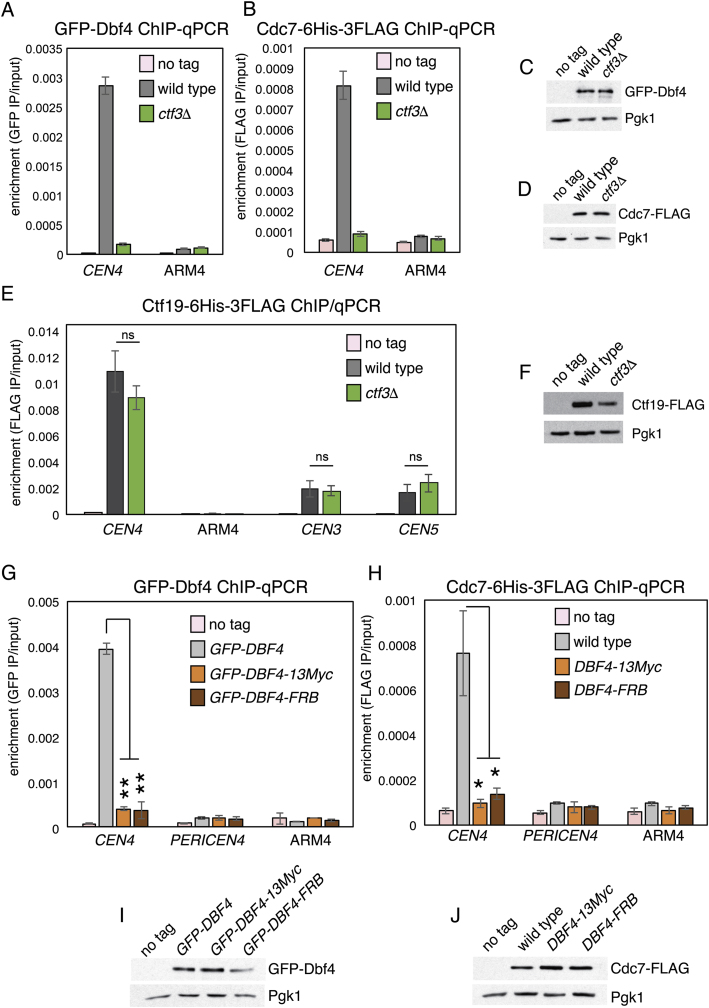
Figure S4.
DDK Recruitment to Kinetochores Is Abolished in Cells Lacking CTF3 or with C-Terminally Tagged Dbf4, Related to Figure 3
(A and B) DDK localization was assessed by ChIP-qPCR for wild-type and ctf3Δ strains. Wild-type and ctf3Δ cells carrying GFP-DBF4 (AM21871 and AM23275, respectively; panel A) or CDC7-6His-3FLAG (AM21110 and AM23268, respectively; panel B), together with an untagged control strain (AM1176) were arrested in G1 for 3h before harvesting for ChIP-qPCR. Means of three independent experiments are shown (error bars – standard error).
(C and D) Immunoblots showing levels of GFP-Dbf4, Cdc7-FLAG and Pgk1 (loading control) in the samples from a representative experiment.
(E) Ctf19 localization was assessed by ChIP-qPCR for wild-type and ctf3Δ strains. Wild-type and ctf3Δ strains carrying CTF19-6His-3FLAG were arrested in metaphase by treatment with nocodazole and benomyl and ChIP-qPCR experiments were performed as in Figure 5F.
(F) Immunoblot showing levels of Ctf19-6His-3FLAG and Pgk1 (loading control) for the indicated strains.
(G and H) DDK localization was assessed by ChIP-qPCR for strains expressing C-terminally tagged Dbf4. Wild-type cells and those in which Dbf4 bears a C-terminal 13Myc or FRB tag and carrying GFP-DBF4 (AM21871, AM22226, and AM22230, respectively; panel E) or CDC7-FLAG (AM21110, AM22538, and AM22540, respectively; panel F), along with an untagged control strain (AM1176), were arrested in G1 for 3h before harvesting for ChIP-qPCR. The means of three independent experiments are shown (error bars – standard error; ∗ – p < 0.05; ∗∗ – p < 0.01; Student’s t test, paired, two-tails).
(I and J) Immunoblots showing relative levels of GFP-Dbf4, Cdc7-FLAG and Pgk1 (loading control) in the samples from a representative experiment.