Fig. 1.
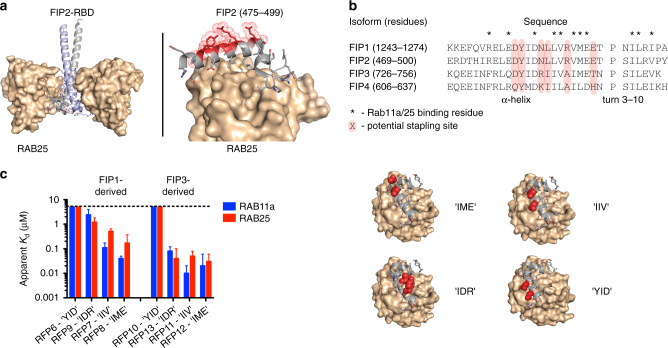
Development of stapled peptide ligands targeting RAB11a and RAB25. a Crystal structure of the RAB25:FIP2 heterotetramer (left). The C-terminal RAB-binding domain of FIP2 binds as a helix-turn-helix peptide (gray and blue) to a hydrophobic groove on RAB25 (tan surface). Side chains not involved in RAB25 binding are highlighted as red surfaces while others are shown as sticks (right). PDB accession: 3TSO. b Sequence alignment of the RAB-binding domains from Class-I (FIP1 and 2) and Class-II (FIP3 and 4) FIP proteins. Residue annotations were assigned based on published RAB11a:FIP3 and RAB25:FIP2 crystal structures. c Graphical depiction of apparent affinities for initial series of FIP1- and FIP3-derived stapled peptides for binding to both RAB11a and RAB25. Each peptide stapling position is denoted by the residues in FIP3 spanned by the hydrocarbon staple (e.g., “IIV”), highlighted in red on the schematic structures shown (right). The affinity graphs show the mean apparent K d with error bars representing the 95% confidence interval from triplicate replicates and application of a sigmoidal curve fit using Prism 5 software