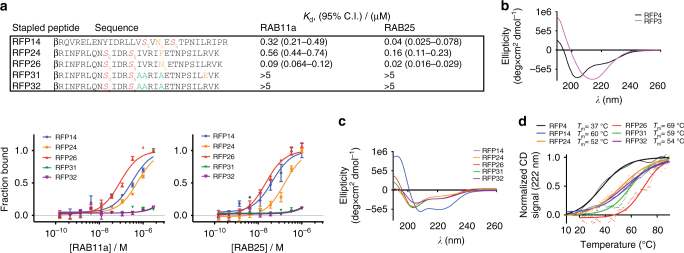
Fig. 2.
Optimized stapled peptides targeting RAB25 show correlated structural stability and high-affinity binding. a Fluorescence polarization binding curves for three lead compounds, RFP14, 24, and 26, as well as two negative control peptides, RFP31 and 32, to both RAB11a and RAB25 (bottom). Sequences and calculated apparent K d values are shown (top). Residues highlighted in yellow denote potential gain-of-function mutations to RAB-binding positions, while those in green denotes loss-of-function alanine replacement of hydrophobic RAB-binding side chains for the negative controls. b Circular dichroism (CD) spectra of unmodified peptides derived from the RBD of FIP3 and FIP4. c CD spectra of optimized RFP stapled peptides. d Thermal denaturation CD curves measuring relative helical content (CD absorbance at 222 nm) of the indicated peptides over a temperature range from 10 to 90 °C. Individual data points at one-degree increments are shown with a sigmoidal curve fit overlay. Binding data points represent the mean ± s.e.m. from triplicate measurements. Affinities listed represent the mean apparent K d with 95% confidence interval from triplicate replicates and application of a sigmoidal curve fit using Prism 5 software. β, beta-alanine