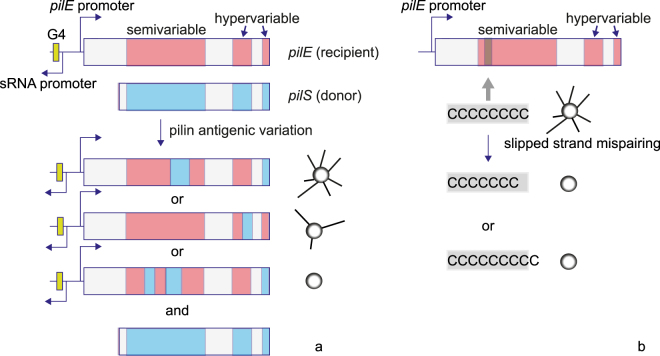
Figure 1.
Pilin antigenic and phase variation. (a) Antigenic variation. The gene encoding for the major pilin subunit pilE contains semi- and hypervariable regions. Silent, promoter-less copies of the pilin, pilS, containing different sequences can partially recombine into the pilE recipient. This process depends on the G4 motif and recA. The pilin sequence of the resulting variant is modified and often non-functional, generating non-piliated variants41. (b) Phase variation due to homopolymeric repeats. Various genes involved in T4P biogenesis and post-translational modification contain homopolymeric stretches within their ORFs. Through slipped-strand mispairing during replication, the homopolymeric stretch is extended or truncated by a nucleotide at high probability and the gene is switched off.