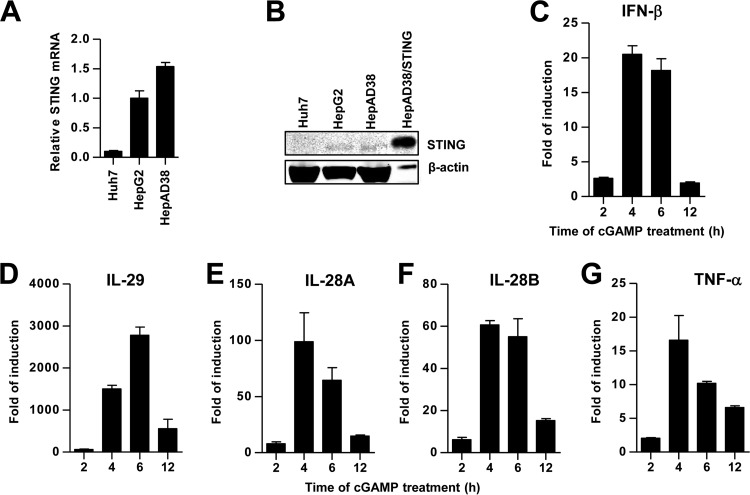
FIG 3.
Expression and functionality of STING in human hepatoma cells. The relative levels of STING mRNA (A) and protein (B) in the human hepatoma cells were determined by qRT-PCR and Western blot assays, respectively. The amounts of STING mRNA detected in each of the cell lines were normalized to β-actin mRNA and are expressed as relative levels to that in HepG2 cells. For the Western blot assay, a HepAD38-derived stable cell line expressing human STING (HepAD38/hSTING) was used as a positive control. β-Actin served as a loading control. Compared to other cells, one-tenth of the cell lysate from HepAD38/hSTING cells was loaded. (C to G) HepG2 cells were mock treated or treated with cGAMP at 10 μg/ml for 30 min and then harvested 2, 4, 6, and 12 h posttreatment. The levels of IFN-β, IL-29, IL-28A, IL-28B, and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) mRNA were determined by qRT-PCR assays and normalized to β-actin mRNA and are expressed as the fold of induction over that in mock-treated controls. Means and standard deviations are presented (n = 2 to 4).