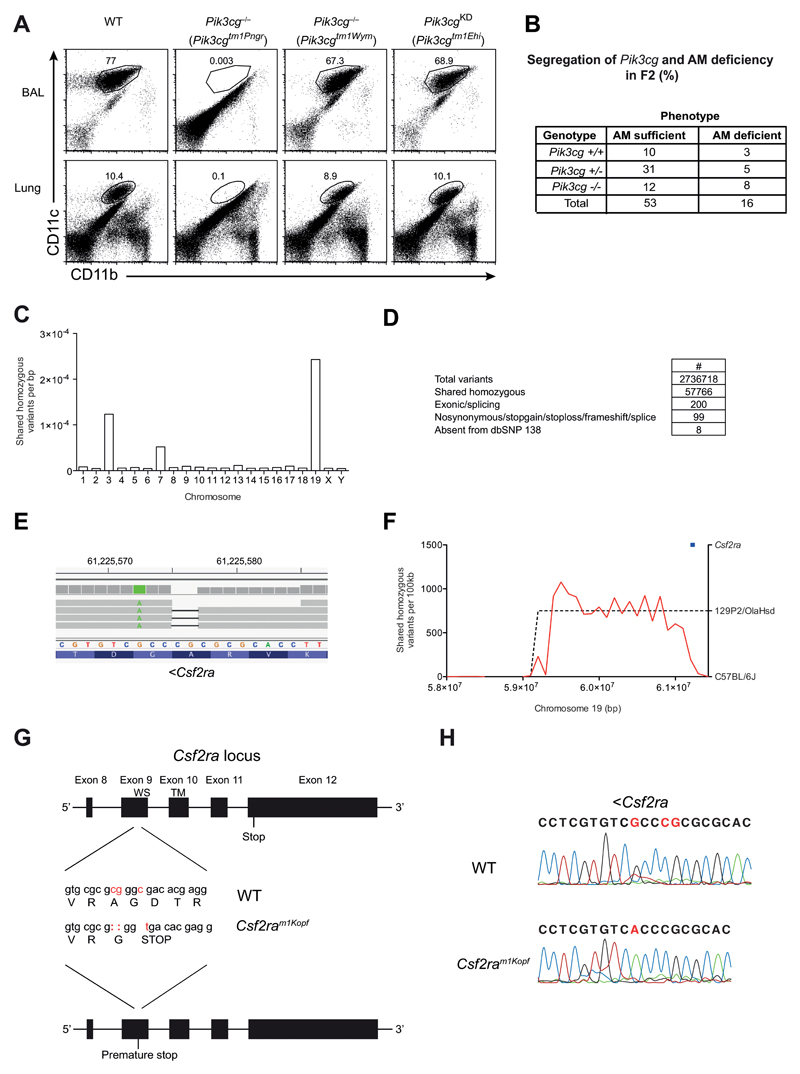
Figure 2. AM deficiency is independent of PI3Kγ but caused by mutated Csf2ra gene.
(A) Flow cytometry of AMs in BAL fluid and lungs of C57BL/6, Pik3cg–/– (Pik3cgtm1Pen and Pik3cgtm1Wym) and Pik3cgKD (Pik3cgtm1Ehi) mice, gated on CD45+ cells. Numbers adjacent to outlined areas indicate percent CD11c+CD11bint AMs. (B) WT, Pik3cg–/– (Pik3cgtm1Wym) were infected i.t. with 50 PFU influenza A virus PR8 and their survival was monitored. (C) Pik3cgtm1Pen-/- mice were backcrossed once onto C57BL/6 (F1). Shown is a table containing the F2 offspring of the F1xF1 intercross with their Pik3cg genotype and AM phenotype for all analyzed mice. (D) The frequency of homozygous variants shared between three alveolar macrophage-deficient mice. (E) Filtering pipeline for variants detected by whole-genome sequencing. (F) IGV view of the homozygous Csf2ra 2bp deletion. A neighboring point mutation is indicated in green. (G) Density of shared homozygous variants (plotted as a red line) on the distal end of chromosome 19. The region of high density (indicated by a dashed line) represents a haplotype derived from the 129P2/OlaHsd background. The Csf2ra locus is indicated in blue. (H) The last 5 exons of the Csf2ra locus are depicted. The mutations in the Csf2ram1Kopf mouse strain are displayed in red and the resulting changes in the amino acid sequence are indicated (WS, WSXWS motif; TM, transmembrane domain). (I) Sanger sequencing results of the Csf2ra region encoding the mutation.