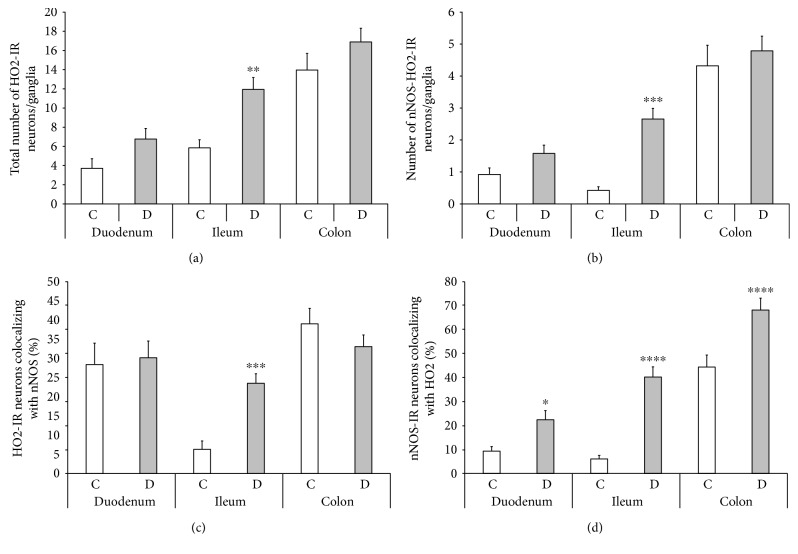
Figure 6.
Quantitative evaluation of the total number of HO2-IR neurons (a), the number of nNOS-HO2-IR neurons (b), the proportion of HO2-IR neurons colocalizing with nNOS (c), and the proportion of nNOS-IR neurons colocalizing with HO2 (d) in the myenteric ganglia of the duodenum, ileum, and colon of control and diabetic rats. The total number of HO2-IR neurons and the number of nNOS-HO2-IR myenteric neurons largely increased in the ileum of diabetic rats. The percentage of HO2-IR neurons colocalizing with nNOS was elevated only in the diabetic ileum. However, the proportion of nNOS-IR neurons colocalizing with HO2 was enhanced in each gut segment of diabetics. The largest increase, more than 6-fold, was observed in the ileal ganglia. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001 (between controls and diabetics). C: controls; D: diabetics.