Fig. 6. Compound 521.
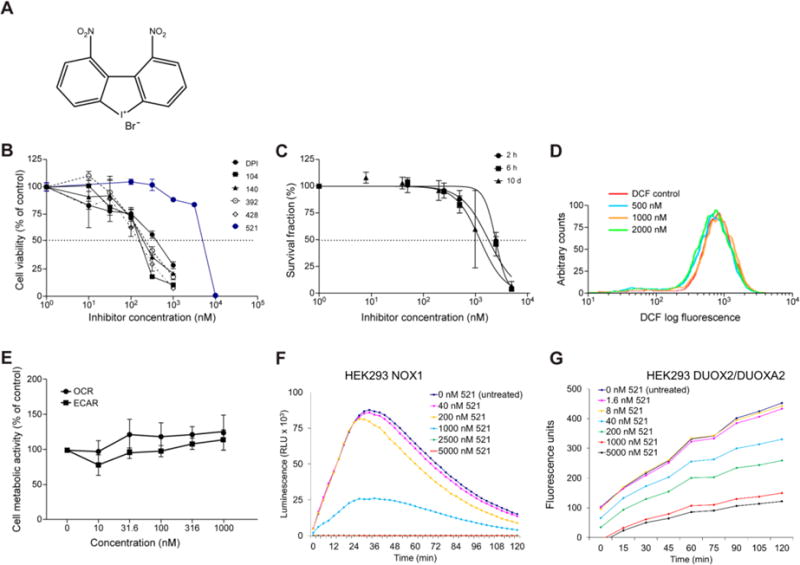
The inhibitory effects of 521 on HT-29 cell growth, whole-cell ROS production, cellular respiration, and extracellular ROS production were assessed using the same methods described above for the other DPI analogs. (A) Chemical structure of NSC 780521. (B, C) Concentration-dependent inhibition of HT-29 cell proliferation after 72-h exposure (B), measured by MTT assay; and of colony formation after 2 h, 6 h, or 10 days of HT-29 cell exposure to compound 521 (C). (D) Effect of 24-h treatment with 521 on intracellular ROS production in HT-29 cells, measured by analytical cytometry using the redox-sensitive dye CM-H2-DCF-DA. (E) Effect of compound 521 on cellular metabolism following 24-h exposure evaluated by measuring oxygen consumption rates (OCR) and extracellular acidification rate (ECAR), respectively, with the Seahorse Extracellular Flux Analyzer; (F, G) PMA-induced extracellular ROS production measured by luminescence assay and Amplex Red assay in NOX1 (baseline O2•− production rate = 1.37 × 10−2 RLU/min/cell) and DUOX2/DUOXA2 overexpression stable HEK293 cells (baseline H2O2 production rate = 1.0 × 10−4 RFU/min/cell), respectively, treated with 521 for 30 min. Data in panels B, C, and E represent the mean ± SD (error bars) of at least three experiments. RLU, relative light units; RFU, relative fluorescence units.
