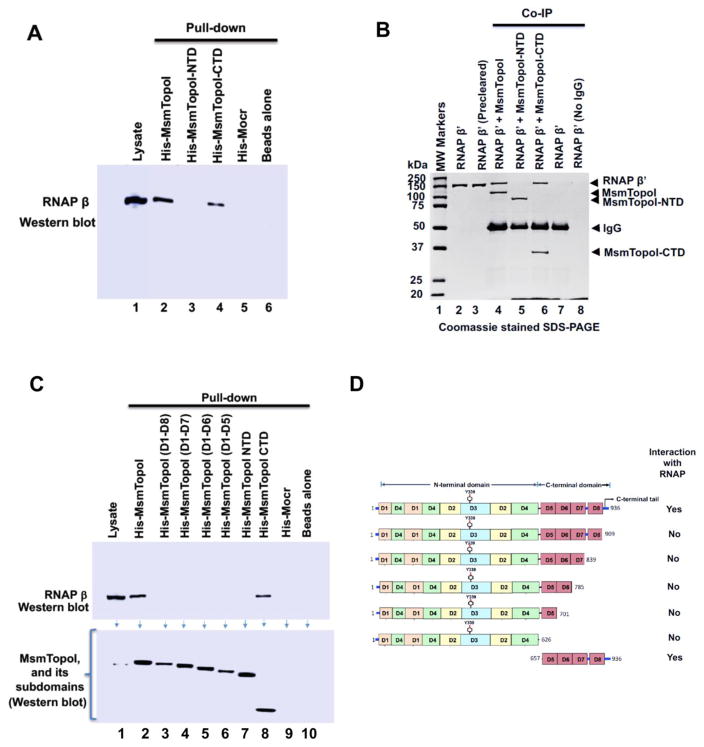
Figure 5. Identification of MsmTopoI sequence required for interaction with RNAP.
(A) M. smegmatis soluble lysate was incubated with the His-tagged recombinant MsmTopoI or its fragment, and the eluates from the reaction were analyzed by western blotting. TopoI-CTD, but not TopoI-NTD, can interact with RNAP in M. smegmatis cell lysate. (B) Direct physical interaction between TopoI-CTD and RNAP β′ subunit was verified by Co-IP assay. Purified RNAP β′ subunit was incubated with MsmTopoI or its fragment, and the proteins immunoprecipiated by TopoI antibodies from the reactions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE/coomassie staining. The assay confirms a physical interaction of RNAP β′ with MsmTopoI-CTD (lane 6), and not MsmTopoI-NTD (lane 5). Purified RNAP β′, by itself, did not bind to the antibody (lane 7) or the beads (lane 8). (C) Pull-down assay with MsmTopoI truncation mutants lacking different segments of the TopoI-CTD. M. smegmatis soluble lysate was incubated with different constructs of the recombinant MsmTopoI, and the eluates were probed for the presence of RNAP. The full-length recombinant MsmTopoI (lane 2), and CTD-MsmTopoI (lane 8) can interact with RNAP. (D) Domain arrangement of MsmTopoI is shown here. The results from pull-down and Co-IP assays, taken together, demonstrate that the tail at the C-terminal end of MsmTopoI interacts with RNAP.