Fig. 5. Verification of RNase HI and RNase HII rN-DNA substrate specificity in vitro and the rN-density in DNA of the RNase H+ cells and rnh mutants.
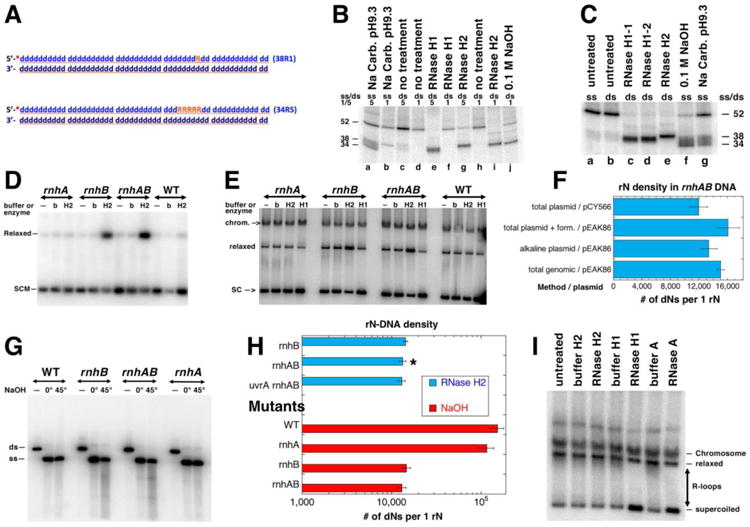
A. A scheme of the two double stranded oligo substrates: 38R1 (single rN) and 34R5 (five consecutive rN). The 32P label at the 5′ end is shown as a red asterisk. DNA nucleotides are shown as blue lower case “d”, ribonucleotides are orange uppercase “R”. B. Products of the rN-DNA substrate hydrolysis by E. coli RNase HI and RNase HII enzymes. The radiolabelled rN-containing dsDNA oligos (shown in A) were incubated with the RNase HI or RNase HII enzymes. “0.1 M NaOH” and “Na Carb. pH 9.3” refer to alkali conditions in which rN hydrolysis produces reference size products. Numbers “1” or “5” refer to 38R1 or 34R5 oligos (A); ss/ds refers to whether the substrate used in the reaction was single-stranded or double-stranded. RNase H1 and RNase H2 were the E. coli enzymes RNase HI and RNase HII. RNase H1-1 and RNase H1-2 were RNase HI enzymes from different producers. The numbers on the side of the gel represent the sizes of the substrate and cleavage products. The reaction products were analyzed in 18% urea-PAGE gel. C. Only 34R5 oligo was used as either ss or ds substrate. All designations are like in “B”. D. Treatment with RNase HII of the plasmid isolated by alkaline lysis protocol. SCM, supercoiled monomer; b, buffer; H2, RNase HII. Plasmid: pEAK86, plasmid isolation was done at 0°C. Strains for results shown in panels D-I were: WT, AB1157; rnhA, L-413; rnhB, L-415; rnhAB, L-416; uvrA rnhAB L-417. Product of the reactions were run in 1.1% agarose gel; autoradiogram of the representative Southern blot with the radiolabelled pEAK86 DNA as a probe is shown here and also in E and G. E. Treatment with either RNase HI or RNase HII enzymes of the plasmid isolated by the total genomic DNA protocol. SC, supercoiled plasmid; relaxed, relaxed plasmid; chrom., chromosomal DNA. Plasmid: pEAK86. Analysis of plasmid species was carried out as in D. F. Summary of quantification of the RNaseHII-revealed density of rNs in plasmid DNA isolated by various methods from the rnhAB double mutant. The density calculations are described in Methods. “Form.”, formamide. G. Alkali treatment analysis of rN-density. The plasmid DNA isolated by alkaline lysis at 0°C, was linearized and treated with NaOH. Treatment: “—”, no treatment; 0°, 0.2 M NaOH, 20 mM EDTA treatment on ice for 20 min; 45°, 0.3 M NaOH, 20 mM EDTA treatment at 45°C for 90 minutes. ds, linearized plasmid DNA, ss -single stranded plasmid. The samples were run in 1.1% agarose in TAE buffer, at 4°C. H. Summary of quantification of the rN-density determined by either RNase HII or by alkali treatments (from gels like in “G”). Various mutant comparison data are shown, pEAK86 was purified by alkaline lysis only, values are means of three independent measurements ± SEM. The star identifies the value already reported in panel “F”. I. R-loop removal by RNase HI or by RNase A. pAM34 isolated from rnhA (strain L-413) by the total genomic DNA protocol.
