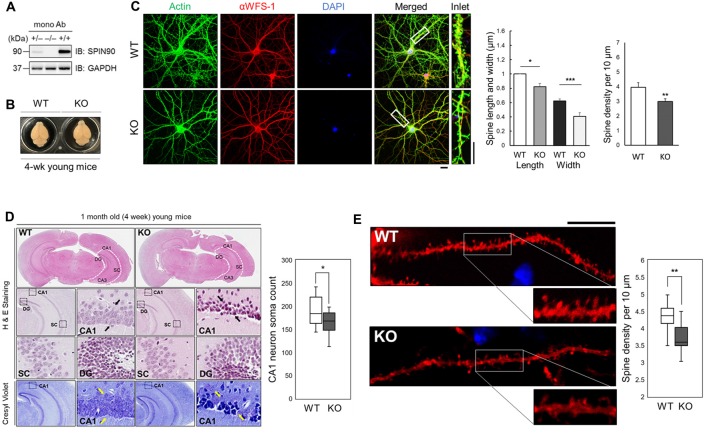
Figure 1.
SH3 protein interacting with Nck 90 kDa (Spin90) deletion disrupts spine morphology and CA1 hippocampal structure. (A) SPIN90 expression in wild-type (+/+), heterozygous (+/−) and knockout (KO) (−/−) homozygous mice. Western blot analysis of brain tissues from each genotype detected with monoclonal SPIN90 antibody. (B) Exterior gross morphology of wildtype (WT) and Spin90-KO mice brains fixed in 1.5% paraformaldehyde (PFA). (C) Immunocytochemistry of DIV18–21 cultured hippocampal neurons stained by CA1 neuron marker, αWFS1 (red), phalloidin (green) and DAPI (blue). Scale bars represent 20 μm (short) and 10 μm (long). Statistical analysis of spine length and width (in μm) (n = 27–33) and spine density (n = 36–44). (D) Histological assessment of WT and Spin90-KO hippocampal slices by H&E and cresyl violet staining. CA3, CA1, DG, SC subregions were qualitatively assessed. Black arrows indicate structural differences in soma distribution in each region of the hippocampus. Yellow arrows indicate loss of soma in CA1. Quantitative cell count of CA1 soma analysis (n = 13 for both genotypes). (E) Spine density analysis in CA1 neurons of DiI labeled WT or Spin90-KO hippocampal slices. Spine density was determined by dividing the number of spines per 10 μm dendrite (n = 49 for WT, n = 54 dendritic segments for Spin90-KO). Scale bar and white box length are 10 μm. All data are expressed as means ± SEM (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001).