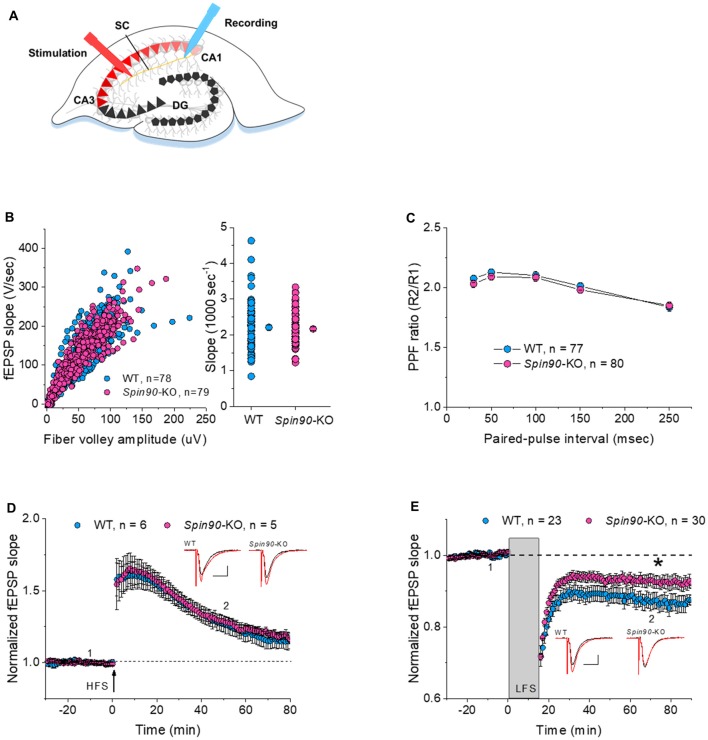
Figure 2.
Normal synaptic transmission and long-term potentiation (LTP), but impaired long-term depression (LTD), in Spin90-KO mice. (A) Schematic diagram of extracellular field recordings on WT (+/+) and Spin90-KO (−/−) hippocampi. CA3 region of slices was stimulated by electrodes, and signals propagated through the Schaffer Collateral (SC) axons to the CA1 region were recorded as EPSPs. (B) Synaptic input-output relationship obtained by plotting the slopes of evoked field excitatory postsynaptic potentials (fEPSPs) against fiber-volley amplitude (n = 78 for WT, n = 79 for Spin90-KO). (C) Ratios of paired-pulse facilitation (PPF) plotted as a function of paired-pulse interval (n = 77 for WT, n = 80 for Spin90-KO). (D) Representative traces from individual CA1 neurons following HFS stimulation showing normal N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR)-dependent LTP in Spin90-KO neurons. NMDAR-LTP induced by four theta-burst protocol in young CA1 hippocampal slices. The insets are example average traces for 2 min. Baseline trace (black) and LTP trace (red) were collected at 1 and 2, the time points indicating 10 min before and 50 min after LTP induction, respectively. Scale bars, 10 ms and 150 μV (n = 6 for WT; n = 5 for Spin90-KO). (E) NMDAR-LTD was induced by low-frequency stimulation (LFS) at CA1 neurons in WT and Spin90-KO slices. The insets are example average traces for 2 min. Baseline trace (black) and LTD trace (red) were collected at 1 and 2, the time points indicating 10 min before and 55 min after LTD induction, respectively. Scale bars, 10 ms and 150 μV (n = 23 for WT; n = 30 for Spin90-KO). Data are represented as mean ± SEM (*p < 0.05).