Figure 7.
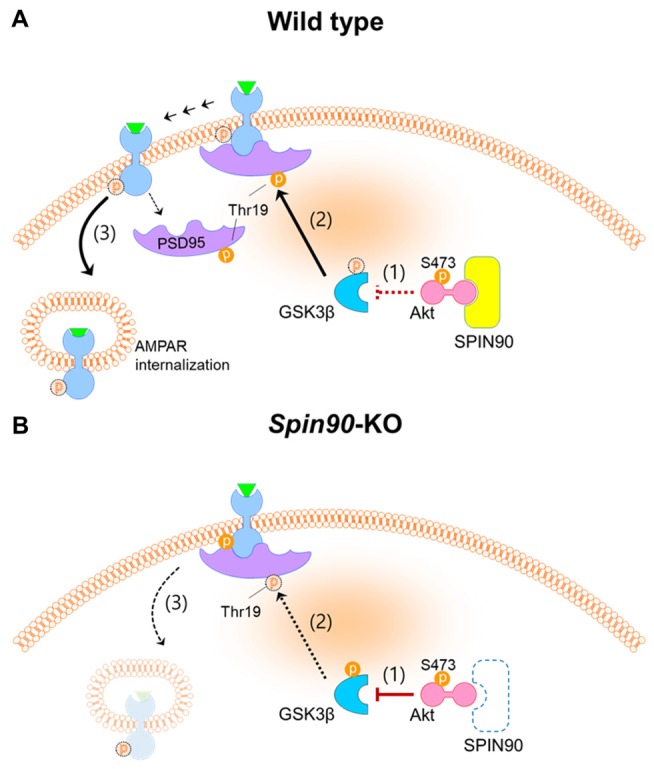
Schematics of SPIN90 during NMDAR-LTD. (A) LTD induction in normal (WT) neurons; (1) Upon NMDAR stimulation, SPIN90 binds to Akt, sequestering it from phosphorylating downstream GSK3β. (2) Active GSK3β is able to phosphorylate PSD95 at Thr19, which causes (3) PSD95 to dissociate from GluA2-containing AMPAR, which subsequently induces AMPAR internalization and LTD. (B) LTD induction in Spin90-KO neurons; (1) Absence of SPIN90 allows activated Akt (phosphorylation at Ser473 sequesters GSK3β, thereby (2) hindering GSK3β from phosphorylating PSD95. (3) GluA2-containing AMPARs remain “docked” on PSD95, unable to internalize. The defect in AMPAR internalization and LTD in Spin90-KO neurons may consequently have secluded excess AMPARs on the surface, which is apparent in Figures 3A–C.
