Figure 1.
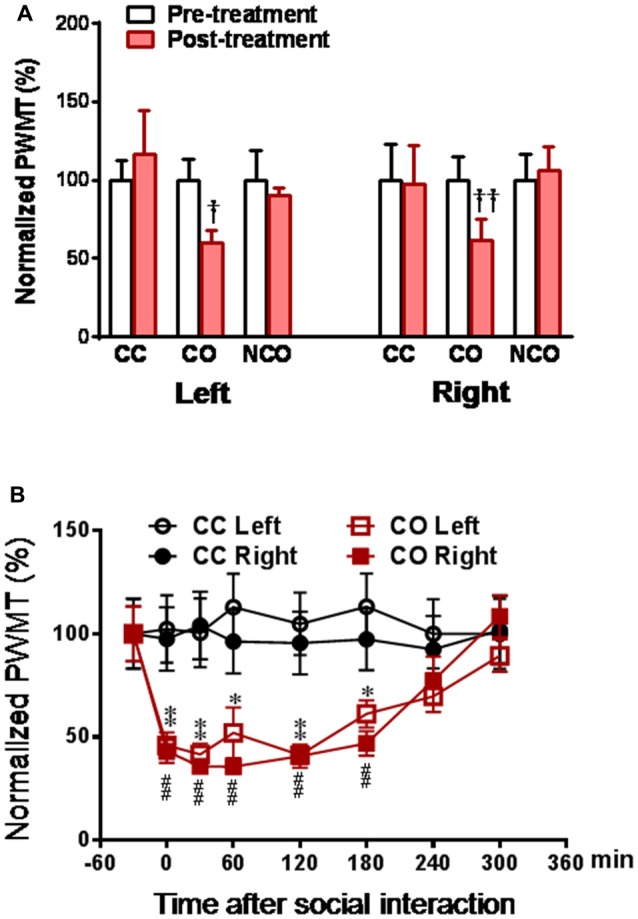
Social interaction with a cagemate in pain induces mechanical pain hypersensitivity in the cagemate observer (CO) rats. (A) showing normalized paw withdrawal mechanical threshold (PWMT) in cagemate control (CC), CO and non-cagemate observer (NCO) rats (n = 6 per group) following 30 min social interaction. Following measurements of PWMT, the lumbar dorsal root ganglia (DRGs) of CC, CO and NCO rats were removed immediately, and then subjected to molecular and biochemical experiments as shown in Figures 3A–C. (B) showing the time course of normalized PWMT in the CC and CO rats (n = 10 per group). CC, cagemate control; CO, cagemate observer; NCO, non-cagemate observer, PWMT, paw withdraw mechanical threshold. †P < 0.05, ††P < 0.01 or *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, or ##P < 0.01, CO vs. CC at each side. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM.
