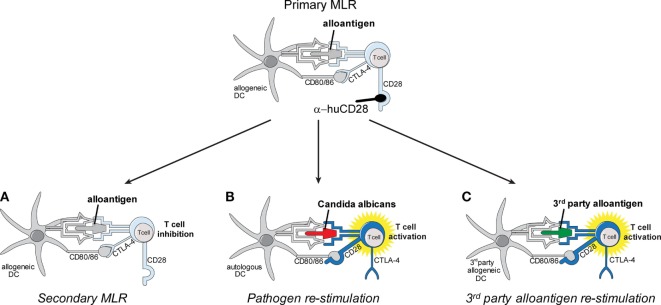
Figure 1.
Schema of in vitro allo-tolerization and retained pathogen reactivity by α-huCD28-mediated blockade of human T-cells. Alloantigen binding to the respective T-cell receptor (TCR) concurrently with CD28 blockade by α-huCD28 potentially tolerizes human T-cells, while CD80/86 co-stimulatory molecules remain accessible to negative regulators such as cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) (top). Human T-cells are co-cultured with MHC-mismatched human dendritic cells (DCs) presenting alloantigen (primary mixed leukocyte reaction), in the presence of the CD28 blocker α-huCD28. After 7 days of culture, T-cells are washed, rested for 2 days in the absence of α-huCD28, and re-stimulated with (A) the same alloantigen (fresh allogeneic DCs), (B) Candida albicans (autologous DCs), or (C) third-party alloantigen (third-party DCs).