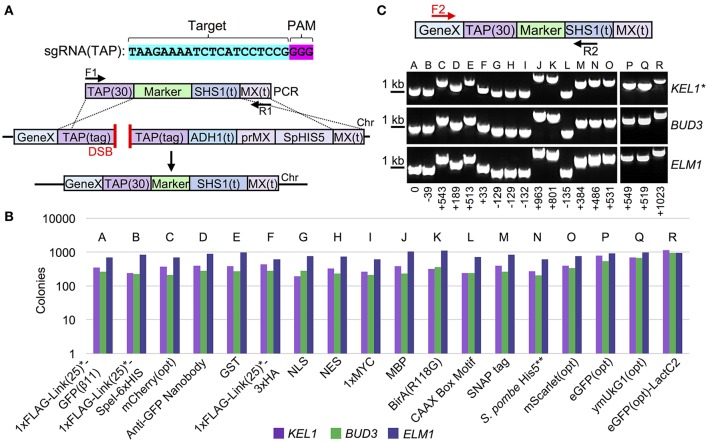
Figure 3.
Collection of C-terminal marker-less tags for Cas9-based integration. (A) The proposed integration strategy illustrated in Figure 2A was used to construct 18 C-terminal peptide or protein fusions (Table 3). (B) TAP-tagged KEL1, BUD3, and ELM1 (GFY-1583, GFY-1589, and GFY-1620) yeast containing Cas9 (pGF-V789) were co-transformed with the sgRNA(TAP) plasmid (pGF-V799) and equimolar amounts of PCR product (F1/R1) amplified from the 18 C-terminal tag constructs (Table 2), selected on SD-URA-LEU plates, and the total colony count quantified for each event. Loss of the native S. pombe HIS5 marker was also assayed (Figure S4). (C) Clonal isolates (n = 1) from each integration (lacking the original HIS5 marker) were assayed by diagnostic PCR (F2, Gene-specific F/R2, “SHS1(t) R”). The relative PCR fragment sizes (bp) are illustrated (setting the first band for PCR “A” as 0 bp). The predicted sizes for PCRs are provided (Table S2). Asterisk, the KEL1 locus was confirmed by DNA sequencing for all 18 integrations.