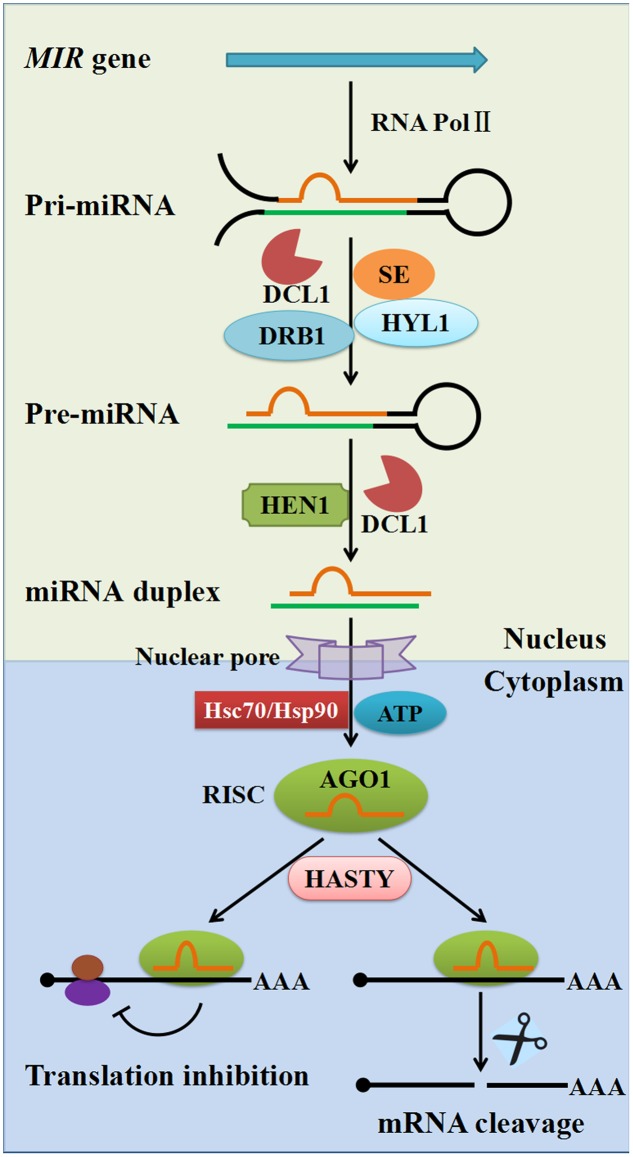
FIGURE 1.
The biogenesis and regulation mechanisms of plant miRNAs. Plant pri-miRNAs are mostly produced from MIR genes by RNA polymerase II (Pol II). Pri-miRNAs are cleaved into pre-miRNAs by DCL1 with the assistance of SE, dsRBP and HYL1. Pre-miRNAs are further processed into 21–24 nucleotide duplex miRNAs by the combined action of DCL1 and HEN1. Duplex miRNAs are methylated by HEN1 into mature miRNA duplexes and are exported to the cytoplasm through the action of plant exportin 5 ortholog HASTY. The guide-strand (red) is then loaded onto an AGO protein with the help of Hsc70/Hsp90 chaperone and ATP, followed by passenger strand (green) ejection, to form a RISC. There are two modes of plant miRNA action in cytoplasm: in one, the miRNA regulates its target at the protein level through translational inhibition (left); in the other, the miRNA regulates its target at the mRNA level through mRNA cleavage (right). AGO1, Argonaute 1; DCL1, Dicer-like1; SE, Serrate; HEN1, Hua enhancer1; DRB1, Double-strand RNA binding protein1; HYL1, Hyponastic leaves1; RISC, RNA-induced silencing complex.