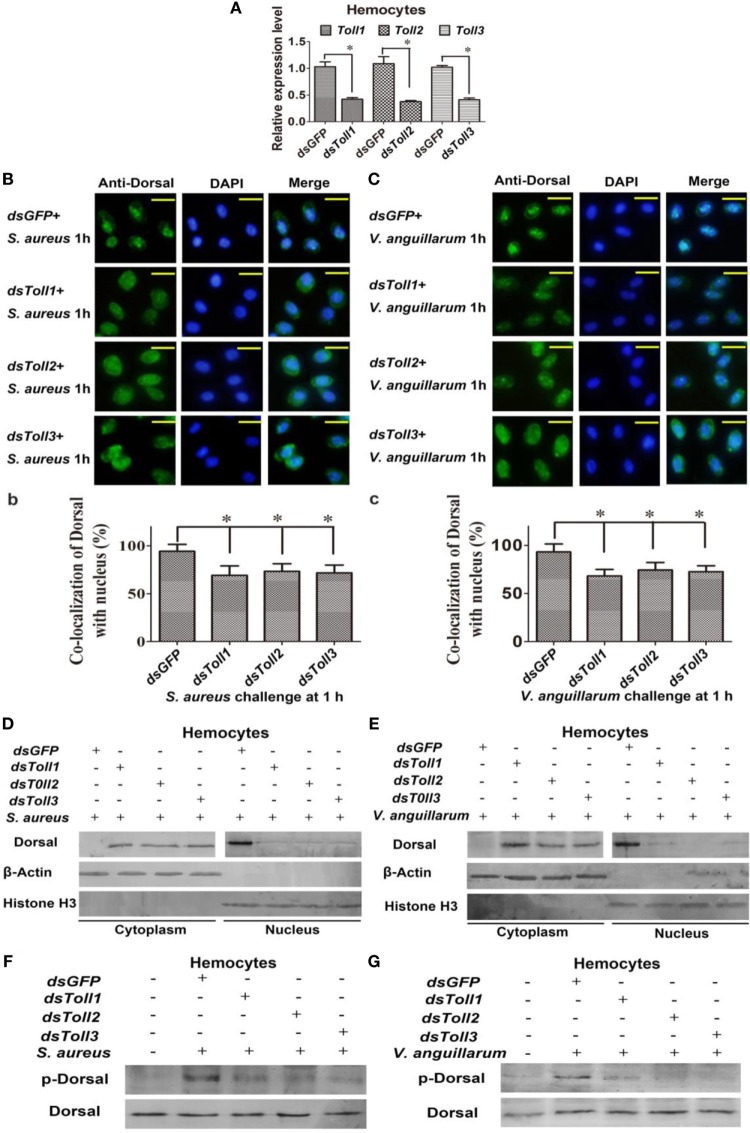
Figure 3.
Toll1–3 regulate Dorsal translocation and phosphorylation. (A) The RNA interference (RNAi) efficiency of Toll1, Toll2, and Toll3 was analyzed by qPCR. (B) Dorsal translocation in hemocytes of Toll1, 2, and 3-silenced shrimp challenged with Staphylococcus aureus was detected using an immunocytochemical assay. (b) Statistic analysis of the colocalization of Dorsal with the nucleus in hemocytes with WCIF ImageJ software. (C) Dorsal translocation in hemocytes of Toll1–3-silenced shrimp challenged with Vibrio anguillarum was analyzed using an immunocytochemical assay. (c) Statistic analysis of the colocalization of Dorsal with the nucleus in hemocytes with WCIF ImageJ software. The dsGFP was used as the control. Significant differences are indicated with asterisks (*p < 0.05). (D,E) Cytoplasmic or nuclear proteins were extracted from the hemocytes of Toll1–3-silenced shrimp challenged with S. aureus (D) or V. anguillarum (E), and the samples were used for western blotting analysis with Dorsal antibody. β-Actin and histone H3 were used as the loading control for the cytoplasmic or nuclear proteins. (F,G) Dorsal phosphorylation was detected in hemocytes from Toll1–3-silenced shrimp challenged with S. aureus (F) or V. anguillarum (G) with phospho-Dorsal antibody. The dsGFP was used as the control.