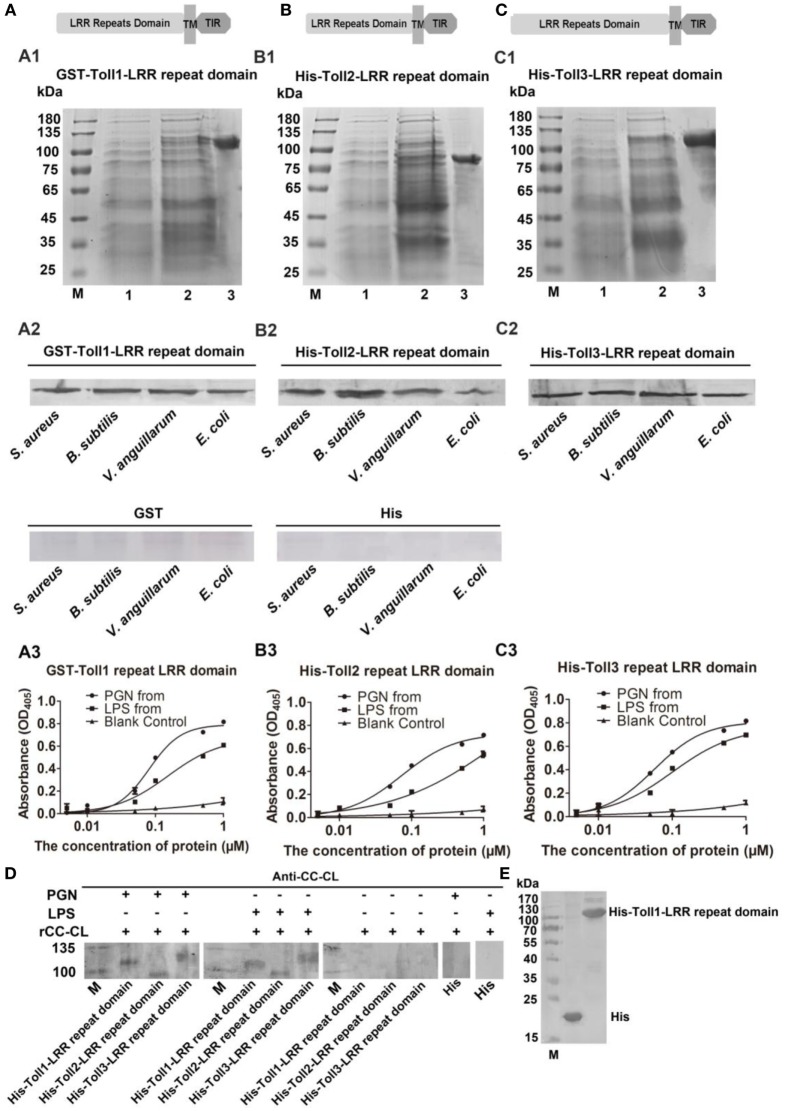
Figure 4.
Recombinant Toll1–3 (rToll1–3) bound to bacteria and polysaccharides. (A–C) Domain architectures of Toll1–3. (A1–C1) The leucine-rich repeat (LRR) domains of Toll1 (A1), Toll2 (B1), and Toll3 (C1) were expressed and purified from Escherichia coli. Lane M, protein marker; lane 1, rToll1–3 proteins of E. coli with recombinant vectors before induction with IPTG; lane 2, rToll1–3 proteins of E. coli with recombinant vectors after induced with IPTG; lane 3, purified protein. (A2–C2) Western blotting analyses were performed to analyze the binding activity of rToll1 (A2), rToll2 (B2), and rToll3 (C2) to different bacteria using anti-His antibody. GST or His was used as negative control. (A3–C3) ELISA was performed to detect the binding activities of rToll1 (A3) rToll2 (B3), and rToll3 (C3) to different polysaccharides [PGN and lipopolysaccharide (LPS)]. (D) A far-Western blotting was used to detect if rToll1, rToll2, and rToll3 could interact with PGN and LPS with anti-CC-CL as first antibody. Purified rTolls were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred into nitrocellulose membrane, respectively. PGN or LPS was incubated with the membrane containing rToll1, 2, or 3. After washed completely, the recombinant CC-CL, a C-type lectin which can bind to LPS and PGN, but could not interact with Toll1–3, was applied on the membrane. Then anti-CC-CL was incubated with the membrane as the first antibody. (E) His and His-Toll1-LRR domains were purified from E. coli.