FIGURE 3.
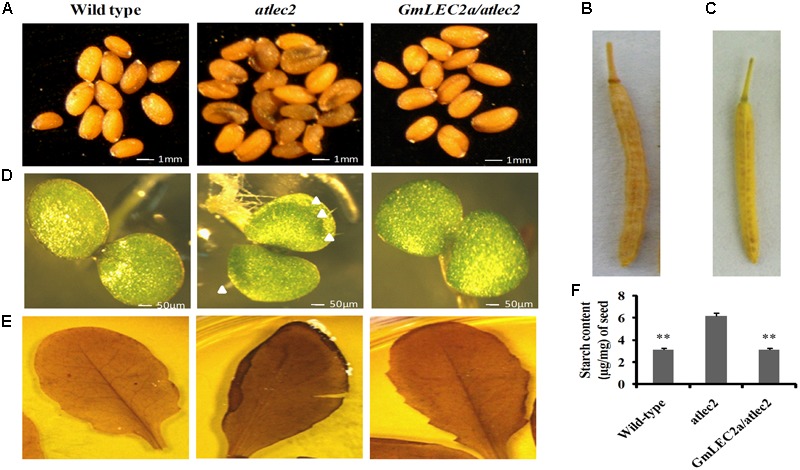
GmLEC2a genetically complements AtLEC2. (A) atlec2 seeds contain more phenolic compounds relative to the wild-type and GmLEC2a/atlec2 complemented seeds. (B) The recovered mature silique length (13 mm) in GmLEC2a/atlec2 complementation plants. (C) The shorter mature silique of atlec2 (∼11 mm) relative to GmLEC2a/atlec2 complementation plants. (D) The abnormal trichomes on adaxial cotyledon surface of atlec2 mutant were restored by expression of GmLEC2a in atlec2 (GmLEC2a/atlec2 complementation). The wild-type, atlec2, and complementation plant seeds were grown on MS media and 4-days old seedlings were photographed. Arrows highlight the trichomes. (E) I-KI Staining of leaf starch, the lec2 mutant leaves were darker when stained with iodine than the wild-type (WS-2) and complementation plant (GmLEC2a/atlec2) leaves indicating high starch content in the leaves.(F) Starch content in WS-2, atlec2, and complementation plant GmLEC2a/atlec2 seeds. The bar represents average of 5 transgenic or control lines. All data are three biological replicates and are expressed as means ± SD. ∗∗P < 0.01 and ∗P < 0.05 by Student’s t-test (n = 3). Asterisks indicate the significant difference relative to the atlec2 mutant.
