Fig. 1.
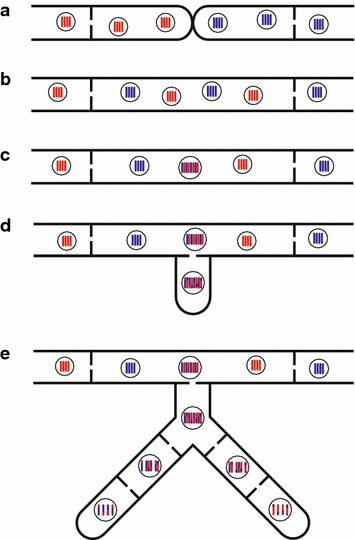
The parasexual cycle. The parasexual cycle parallels events in the sexual cycle, resulting in genetically unique haploid offspring but without a meiotic reduction. a Hyphae of genetically unique homokaryotic parents grow towards each other by chemotaxis and fuse. b Nuclei from each unique strain migrate within the fused hypha, which is now considered a heterokaryon. c Haploid nuclei in the heterokaryon undergo karyogamy to create a heterozygous diploid nucleus. d The diploid nucleus undergoes mitotic recombination to produce a recombined genotype. e In growing hyphae, gradual loss of chromosomes due to repeated rounds of mitotic non-disjunction results in haploidization and unique genotypes in various sectors of mycelium
