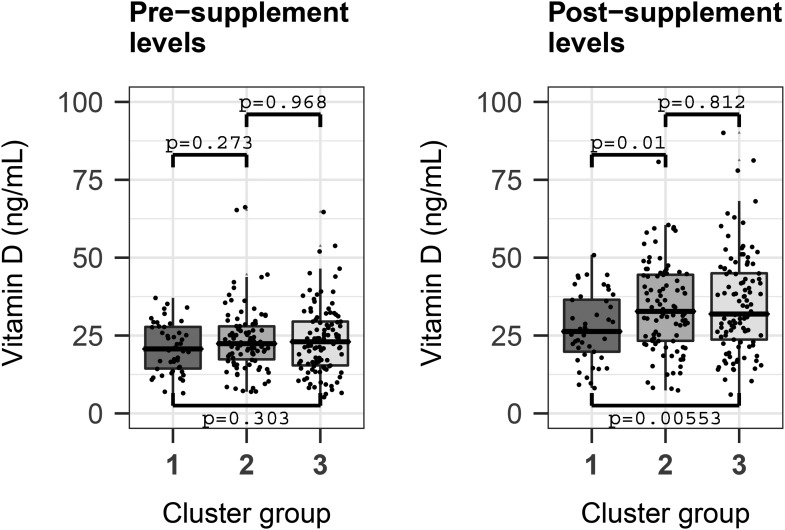
FIGURE 2.
Pre- and postsupplement maternal vitamin D concentrations significantly associate with cluster group segregation. Postsupplement concentrations were significantly lower when cluster group 1 was compared with groups 2 and 3 separately (Mann-Whitney U test). In addition, through a multinomial logistic regression model with sample-to-cluster assignment as outcome and adjusting for significant confounders, sample storage time, maternal age, and education, and the child’s asthma status and vitamin D level at age 3 y, the postsupplement concentration of vitamin D was a significant predictor of cluster grouping (P = 0.0014; OR: 1.032; 95% CI: 1.0021, 1.065). The presupplementation concentration of vitamin D was not a statistically significant predictor of cluster grouping. Presupplementation concentrations (means ± SDs): group 1, 21.10 ± 8.01 ng/mL; group 2, 23.60 ± 10.30 ng/mL; and group 3, 23.60 ± 11.00 ng/mL. Postsupplementation concentrations (means ± SDs): group 1, 27.5 ± 11.0 ng/mL; group 2, 34.0 ± 14.1 ng/mL; and group 3 (35.2 ± 15.9 ng/mL). Total sample N = 245: group 1, 46; group 2, 94; and group 3, 105.