Fig. (1).
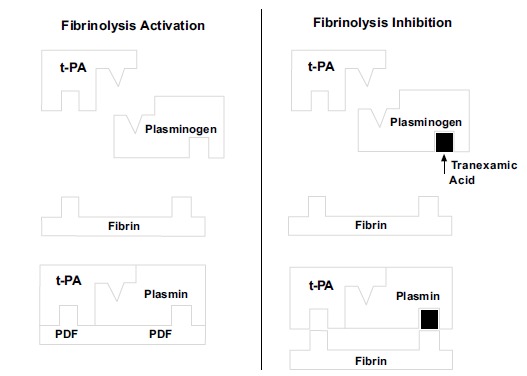
Action mechanism of tranexamic acid (TXA). The site in plasminogen where fibrin binds is occupied by TXA, preventing fibrinolysis. T-PA - Tissue plasminogen activator; FDP - fibrin degradation products. Source: Santos et al. (19).

Action mechanism of tranexamic acid (TXA). The site in plasminogen where fibrin binds is occupied by TXA, preventing fibrinolysis. T-PA - Tissue plasminogen activator; FDP - fibrin degradation products. Source: Santos et al. (19).