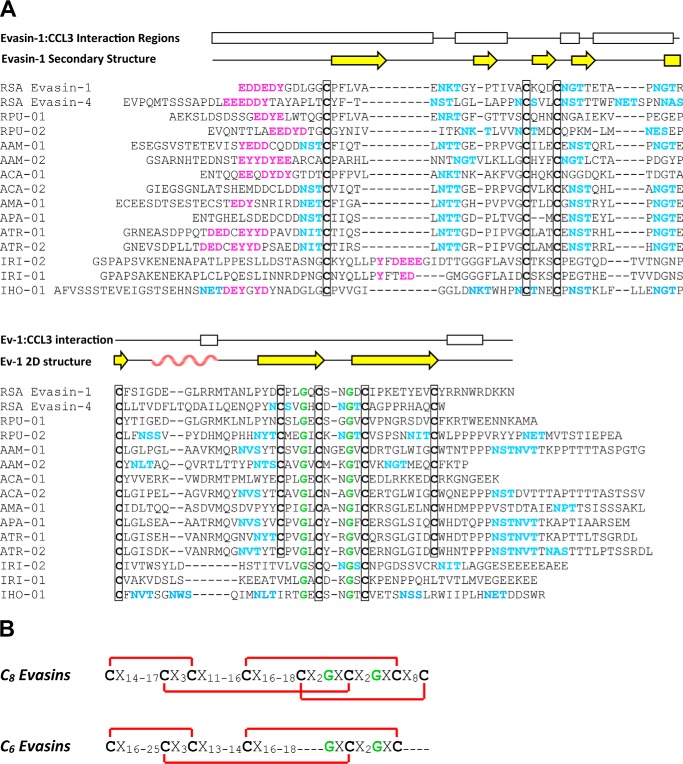
Figure 2.
Features of the evasin protein family. A, multiple sequence alignment (obtained using MUSCLE) of selected evasin candidates with R. sanguineus evasin-1 and -4. Features indicated are conserved cysteines (bold and boxed) and glycines (green), potential N-linked glycosylation sites (cyan), and putative tyrosine sulfation sites (magenta). The secondary structure and regions of evasin-1 that interact with CCL3 in the crystal structure are shown above the alignment; yellow arrows indicate β-strands and the rose wavy line indicates the α-helix. Abbreviations use for tick species are: RSA, R. sanguineus; RPU, R. pulchellus; AAM, A. americanum; ACA, A. cajennense; AMA, A. maculatum; APA, A. parvum; ATR, A. triste; IRI, I. ricinus; IHO, I. holocyclus. B, conserved sequence motifs of the C8 and C6 evasins showing (in red) the disulfide bond connectivity observed in the structure of R. sanguineus evasin-1.