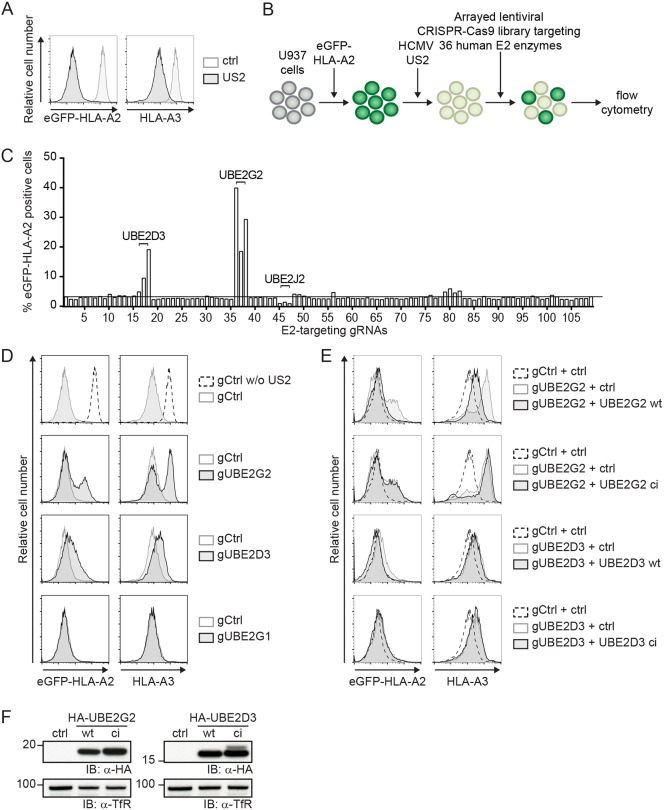
Fig. 1.
A CRISPR/Cas9 library screen for E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes identifies UBE2G2 and UBE2D3 as essential players in US2-mediated HLA-I downregulation. (A) Downregulation of eGFP–HLA-A2 and endogenous HLA-A3 mediated by US2 in U937 cells expressing eGFP–HLA-A2. (B) Schematic overview of the CRISPR/Cas9 library screen to identify E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes essential for US2-mediated HLA-I downregulation. U937 cells are transduced with eGFP–HLA-A2 and subsequently transduced with an HCMV US2 expression vector. As a result, cells display low total eGFP–HLA-A2 expression levels, which can be monitored by means of the eGFP tag. Subsequently, cells are lentivirally transduced with CRISPR/Cas9 constructs targeting individual E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes and selected to purity using puromycin. Cells are analyzed by flow cytometry at 10 dpi to assess total eGFP–HLA-A2 levels. (C) Quantification of the percentage eGFP–HLA-A2-positive US2-expressing cells upon transduction with CRISPR/Cas9 constructs targeting individual E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes. gRNAs targeting UBE2D3, UBE2G2 and UBE2J2 are indicated. (D) CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout of E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes UBE2G2 (gRNA #1) and UBE2D3 (gRNA #3) rescues expression of chimeric eGFP–HLA-A2 and endogenous HLA-A3 from US2-expressing cells. gRNAs targeting UBE2G1 (gRNA #1) were used as a negative control. eGFP–HLA-A2 and endogenous HLA-A3 surface levels were assessed at 10 dpi by flow cytometry. (E) Reconstitution of UBE2G2 or UBE2D3 expression in UBE2G2- and UBE2D3-knockout cells, respectively, rescues US2-mediated downregulation of HLA- I. The wild-type E2 (UBE2G2 wt or UBE2D3 wt) or a catalytically inactive E2 (UBE2G2 ci or UBE2D3 ci) was introduced in the corresponding polyclonal E2 knockout cells from C, after which flow cytometry analysis was performed to assess total eGFP–HLA-A2 levels and endogenous HLA-A3 surface levels at 7 dpi. (F) The expression of wild-type and catalytically inactive E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes used in D was assessed via immunoblotting (IB). Transferrin receptor (TfR) was used as a loading control.