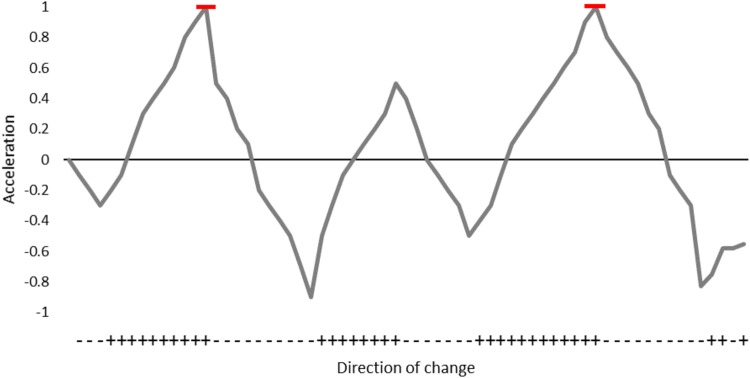
Fig. 3.
Example of how strokes are detected in the accelerometry with an m of 10. If 10 consecutive positive differences either side of a peak in the dynamic acceleration are detected then a stroke is counted. If more than 10 positive or negative differences are detected, then the stroke is identified at the end of the run of positive differences.