Fig. 4.
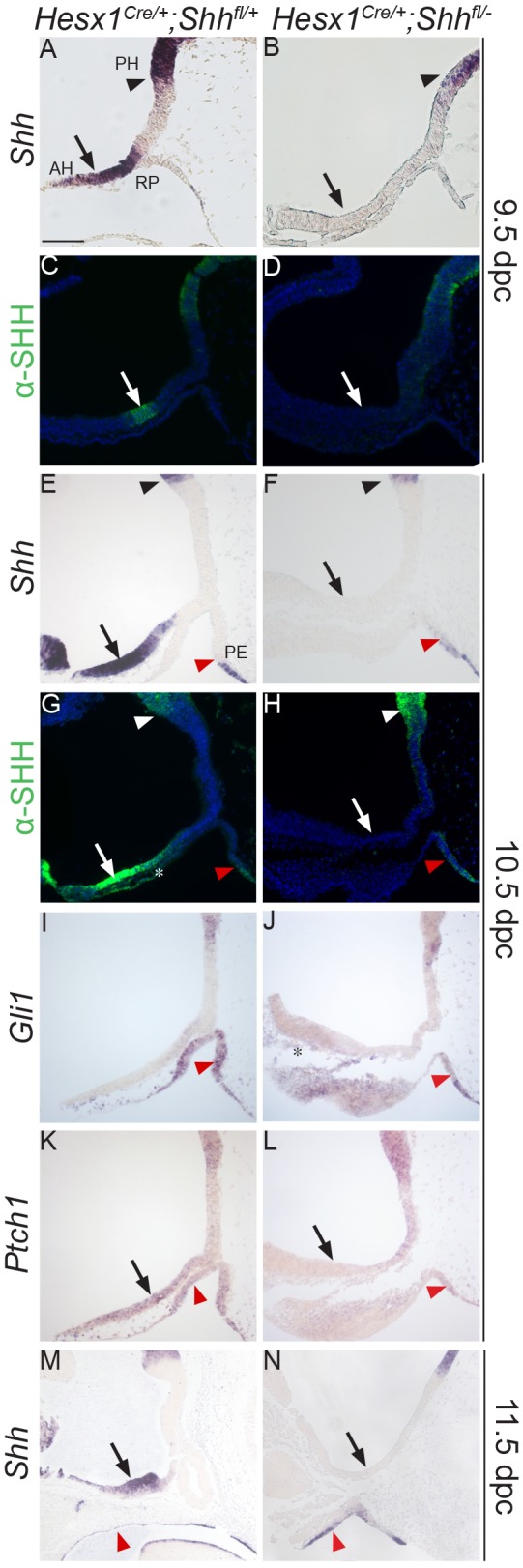
Loss of Shh expression in the anterior hypothalamus of Hesx1Cre/+;Shhfl/− mutants results in reduced Gli1 and Ptch1 expression in the developing Rathke's pouch. (A-H) In situ hybridisation against Shh and anti-SHH immunofluorescent staining on mid-sagittal sections of control and Hesx1Cre/+;Shhfl/− mutant embryos at 9.5 and 10.5 dpc. Expression of Shh transcripts (A,B,E,F) or SHH protein (C,D,G,H) is detected in the anterior and posterior hypothalamus in the control embryos, but is completely undetectable in the AH in the mutant embryos (AH, arrows; PH, black arrowheads). Shh/SHH expression is not detected in the developing RP in the control embryos, but there is ectopic Shh/SHH signal in the posterior region of the developing RP adjacent to the pharyngeal endoderm (PE, red arrowheads) in the mutant RP. (I,J) Gli1 transcripts are strongly detected in the control RP (arrowhead in I), but barely detectable and mostly restricted to the posterior region in the mutant RP (arrowhead in J). Note the Gli1 expression in head mesenchyme underlying the AH in the mutant (asterisk in J). (K,L) Ptch1 expression is lost in the AH (arrows) and developing RP (arrowheads) in the mutant relative to the control embryo. (M,N) Shh transcripts are not detected in the anterior hypothalamus in the mutant embryo (arrows), but are detected throughout the oral ectoderm and pharyngeal endoderm in both the mutant and control embryos (arrowheads). RP, Rathke's pouch; PH, posterior hypothalamus; AH, anterior hypothalamus; PE, pharyngeal endoderm. Scale bar: 100 μm.
