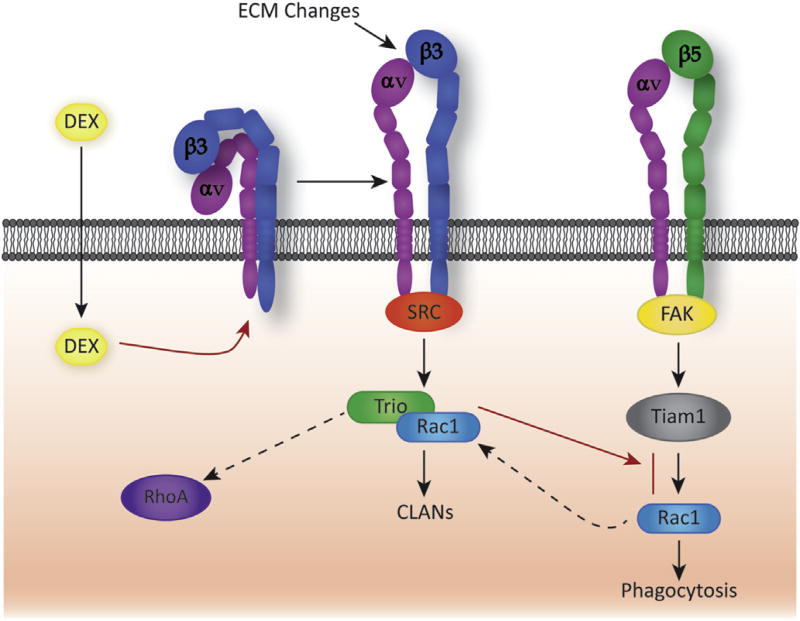
Fig. 6.
Schematic showing differential use of GEFs by αvβ3 and αvβ5 integrins to activate Rac1. In normal human TM cells, αvβ5 integrin uses a Rac1-mediated pathway to induce phagocytosis. The pathway involves focal adhesion kinase (FAK) (Gagen et al., 2013) and the Rac1 specific GEF called Tiam1 (Peotter et al., submitted for publication). Following treatment with dexamethasone, inactive αvβ3 integrins on the cell surface become activated (Filla et al., 2011; Faralli et al., 2013; Gagen et al., 2013) which results in the activation of a Rac1-mediated pathway via the GEF called Trio that promotes the formation of CLANs (Filla et al., 2009; Filla et al., 2011). Utilization of Rac1 by this pathway may inhibit phagocytosis by limiting the availability of Rac1 GEFs as previously reported (Toth et al., 2009; Liu et al., 2013). Interestingly, Trio can act as a GEF for both Rac1 and RhoA (van Rijssel and Van Buul, 2012) which could explain why activation of αvβ3 integrin has recently been reported to activate RhoA (Pattabiraman and Rao, 2015). Use of Trio in this case may represent a way to temporally and spatially coordinate the activity of both Rac1 and RhoA as suggested in studies when both are at activated at the leading edge of migrating cells (Kraynov et al., 2000; Pertz et al., 2006).