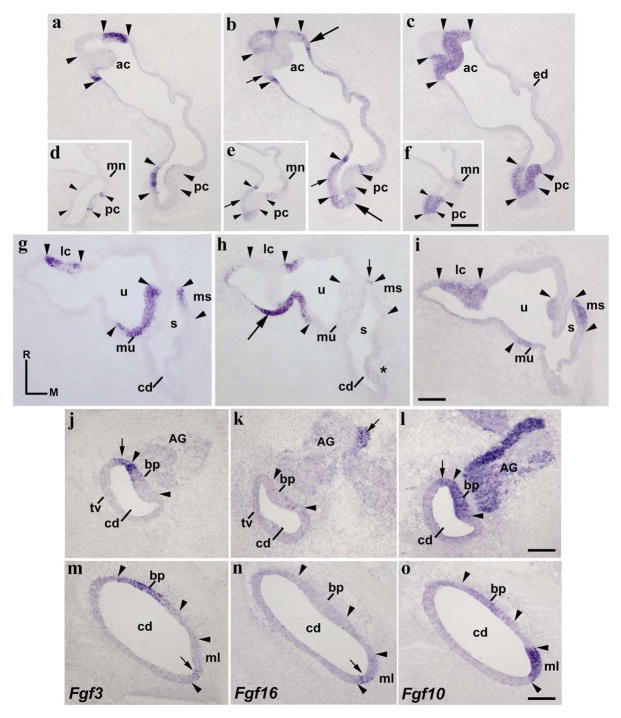
Figure 4. Fgf3 expression pattern at HH34.
Horizontal sections through the inner ear at stage HH34, indicated in Figs 5g and 5h. The probes used are indicated in each column. The borders of each Fgf10-positive sensory elements are indicated by arrowheads. Fgf3 expression was detected in all cristae (ac, lc, and pc; a, d, g). The entire macula utriculi was Fgf3 stained (mu in g). The rostral half of the macula sacculi showed a clear Fgf3 expression (ms in g). In the cochlear duct, the rostralmost portion of the basilar papilla (bp in j, l, m, o) and the contiguous non-sensory epithelium (short arrows in j, l) were Fgf3 positive. The macula lagena showed a few Fgf3-positive cells ventrally (short arrow in m). The Fgf16 expression was observed in the non-sensory epithelium bordering all cristae (long arrows in b, h), as well as in part of the epithelium delimiting the utricular and saccular maculae (short arrows in h for the ms). A few Fgf16-expressing cells were observed in the border of the cristae (short arrows in b). The Fgf3-negative macula neglecta displayed a very weak Fgf16 expression (mn in d, e). Most of the cochlear duct was devoid of Fgf16 transcripts (cd; k, n), except for the macula lagena (ml in n). The acoustic ganglion showed a reduced group of Fgf16-expressing cells (AG; short arrow in k). For the abbreviations, see the list. Orientation: M, medial; R, rostral. Scale bar = 45 μm in f (applies to d–f), 33 μm in i (applies to a–c, g–i), 18 μm in l (applies to j–l), and 14 μm in o (applies to m–o).