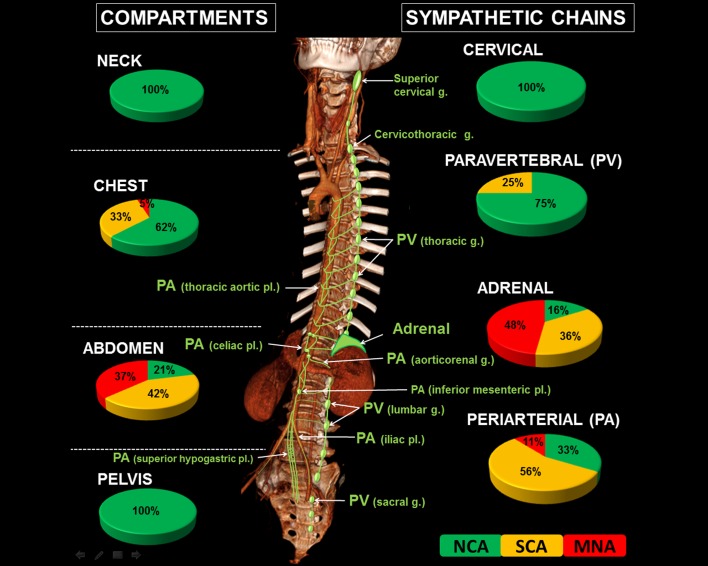
Fig 1. Radiogenomics classification of neuroblastomas according to anatomical origin.
Neuroblastomas may be classified based on the anatomical compartment (i.e., neck, chest, abdomen or pelvis) or according to the sympathetic structure the tumors arise from, i.e., (1) the cervical sympathetic chains (i.e., including the superior, middle and inferior cervical and the cervicothoracic ganglia (g.)); (2) the paravertebral (PV) sympathetic chains (i.e., including all thoracic, lumbar and sacral ganglia); (3) the periarterial (PA) sympathetic pathways (i.e., including the thoracic aortic, abdominal aortic and celiac plexus (pl.)), the aorticorenal ganglia, and the superior and inferior mesenteric, superior hypogastric and iliac plexus); and (4) the adrenal glands. For each compartment or sympathetic group, the pie charts show the distribution of the genomic profile of the tumors, i.e., numerical-only chromosome alterations (NCA), segmental chromosome alterations (SCA) or MYCN amplification (MNA).