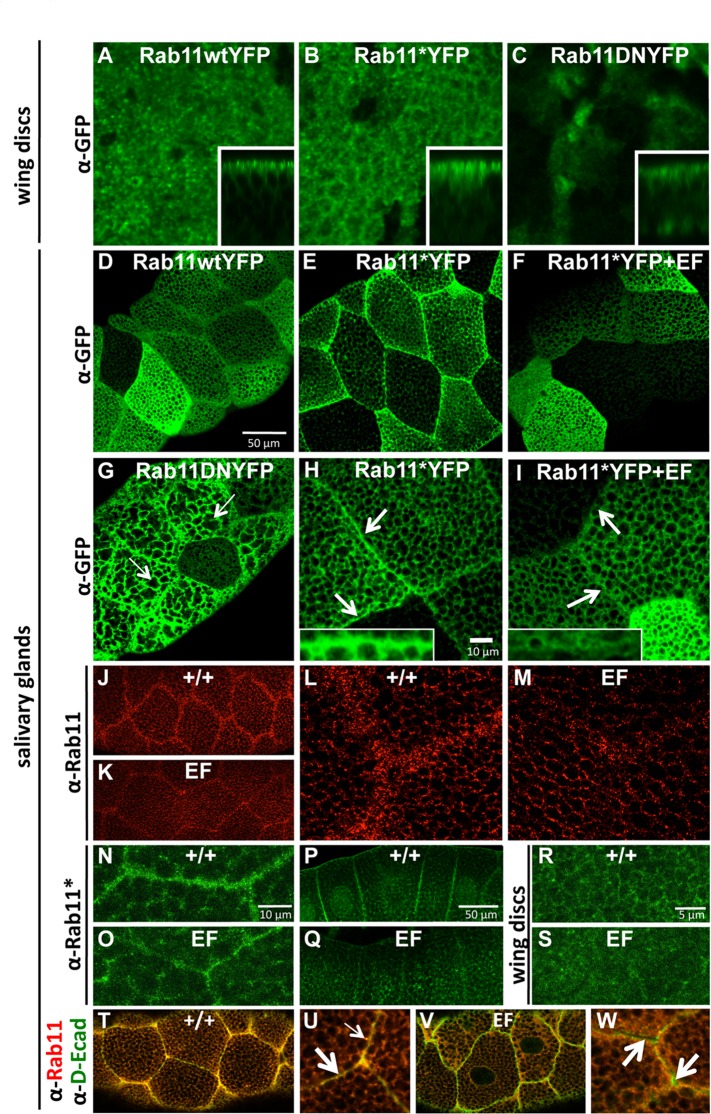
Fig 1. EF inhibits Rab11 downstream of GTP loading.
(A-C) Wing imaginal discs expressing wild-type (wt) and mutant forms of YFP-tagged Rab11, using the strong wing-specific MS1096 GAL4 (abbreviated as 1096GAL4), and stained with a Rabbit anti-GFP antibody, reveal different sub-cellular distributions of Rab11. Insets show corresponding Z-sections. (A) Rab11wt, showing apical restriction. (B) Rab11 activated (or Rab11*), showing apical restriction plus junctional concentration, (C) Rab11 Dominant-Negative (or Rab11DN) showing loss of apical/junctional staining. The bipartite staining of Rab11* is even more pronounced in salivary glands (D-I). (D) 1096GAL4>Rab11wtYFP. (E) 1096GAL4>Rab11*YFP with higher magnification in (H). Arrows point at intercellular junctions where Rab11* accumulates. (F) 1096GAL4>Rab11*YFP +EF. EF blocks Rab11* targeting to the junctions, higher magnification shown in (I). Arrows point to intercellular junctions where Rab11* no longer accumulates when co-expressed with EF. (G) 1096GAL4>Rab11DNYFP, showing that Rab11DN does not concentrate at the junctions, but alters the morphology of secretory granules (thin arrows). (J-M): detection of the endogenous Rab11 reveals that it collects near junctions in a punctate pattern (J), with higher magnification in (L). This preference is abrogated in EF-expressing glands (K), with higher magnification in (M). Selective staining of the activated component of endogenous Rab11 (Rab11*) reveals that this functionally relevant form accumulates next to cell junctions in salivary glands (N), sagittal view in (P), an effect that is reduced in EF-expressing glands (O), sagittal view in (Q). The effect of EF on endogenous Rab11* is also visible in wing imaginal discs: (R) wt, (S) 1096GAL4>EF. Co-labeling of Rab11 and D-Ecad, the Drosophila ortholog of E-Cadherin (T-W) reveals co-localization of Rab11 and D-Ecad at the AJs in wt salivary glands (T), (U) higher magnification. Thick arrow indicates AJs, thin arrow indicates punctate stain near the AJs. Co-localization is lost upon EF expression (V) in salivary glands, (W) higher magnification.