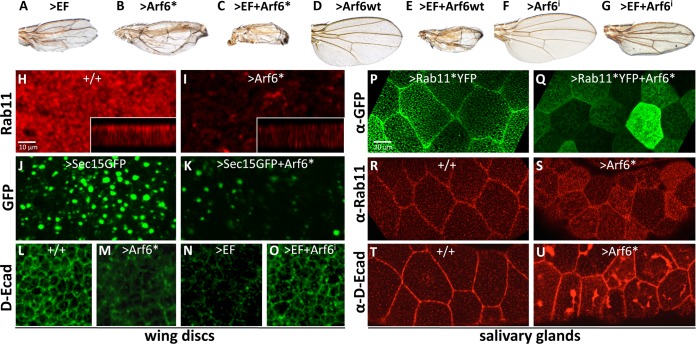
Fig 4. Activation of Arf6 partially mimics the effect of EF.
(A-G) Wings showing EF and Arf6-dependent phenotypes. (A) 1096GAL4>EF. (B) 1096GAL4>Arf6*. Activated Arf6 (Arf6*) causes a phenotype very similar to that caused by EF. (C) 1096GAL4>EF+Arf6*, showing an additive phenotype. (D) 1096GAL4>Arf6wt wing, displaying a wild-type phenotype. (E) 1096GAL4>EF+Arf6wt wing revealing synergy between EF and Arf6wt. (H-I) Wing imaginal discs stained with an anti Rab11 antibody. (H) In wild-type discs, Rab11 displays a dotted apical distribution. (I) In discs expressing Arf6* (1096GAL4>Arf6*), Rab11 levels are reduced, and apical restriction is lost. (J-K) Wing imaginal discs expressing Sec15-GFP. (H) Sec15-GFP expressed at high levels in 1096GAL4>Sec15-GFP discs forms large fluorescent punctae. Like EF, Arf6* expression in (K) 1096GAL4>Sec15-GFP+Arf6* discs blocks formation of Sec15-GFP punctae and reduces Sec15-GFP levels. (L-O) D-Ecad staining in wing imaginal discs. (L) D-Ecad stain in wild-type discs, revealing the apical network of AJs. (M) In 1096GAL4>Arf6* discs, apical D-Ecad levels are severely reduced, an effect similar to that of EF (N). Arf6-RNAi suppresses the EF phenotype and partially restores normal D-Ecad at AJs (O). (P) A 1096GAL4>Rab11*YFP salivary gland showing Rab11* targeting to the AJs, revealed by an anti-GFP stain. (Q) Arf6* blocks Rab11* targeting to cell junctions in 1096GAL4>Rab11*+Arf6* glands. (R) Endogenous Rab11 stain of wild-type salivary glands. (S) Arf6* causes endogenous Rab11 to accumulate in the cytoplasm and diminishes its localization at junctions. (T) D-Ecad stain of wild-type salivary glands. (U) Arf6* results in accumulation of large intracellular inclusions of D-Ecad in 1096GAL4>Arf6* salivary glands.