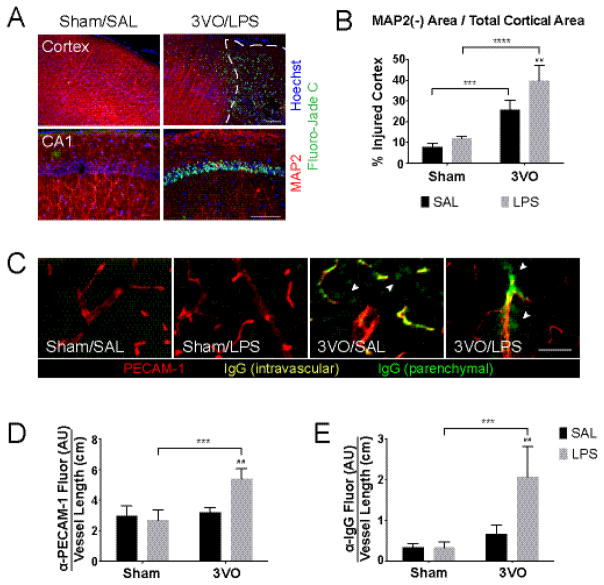
Figure 3.
Effects of systemic LPS exposure on ischemia-induced cortical injury. (A) IHC of coronal brain sections demonstrates combined effects of 3VO/LPS treatment on dendritic injury (beading, loss of MAP2 staining; red) and neuron death (Fluoro-Jade C; green) on cortex (top) and CA1 of the hippocampus (bottom); scale bars = 100 μm. White dashed line outlines area of MAP2(−) cortex. (B) Histogram illustrating exacerbated injury caused by the addition of LPS after 3VO. % Injured cortex = MAP2(−) area, as outlined in (A, top), over total cortical area. (C) Combined 3VO and endotoxemia causes PECAM-1 upregulation (red) and parenchymal IgG deposition (green; white arrowheads); scale bar = 100 μm. 3VO/LPS treatment upregulates vascular PECAM-1 expression (D) and IgG deposition per vessel length (E) in 3VO/LPS animals. Values represent means ± SD (n = 3–4 per group). AU = arbitrary units. 2-way ANOVA: * Sham vs. 3VO; # SAL vs. LPS. ## p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001.