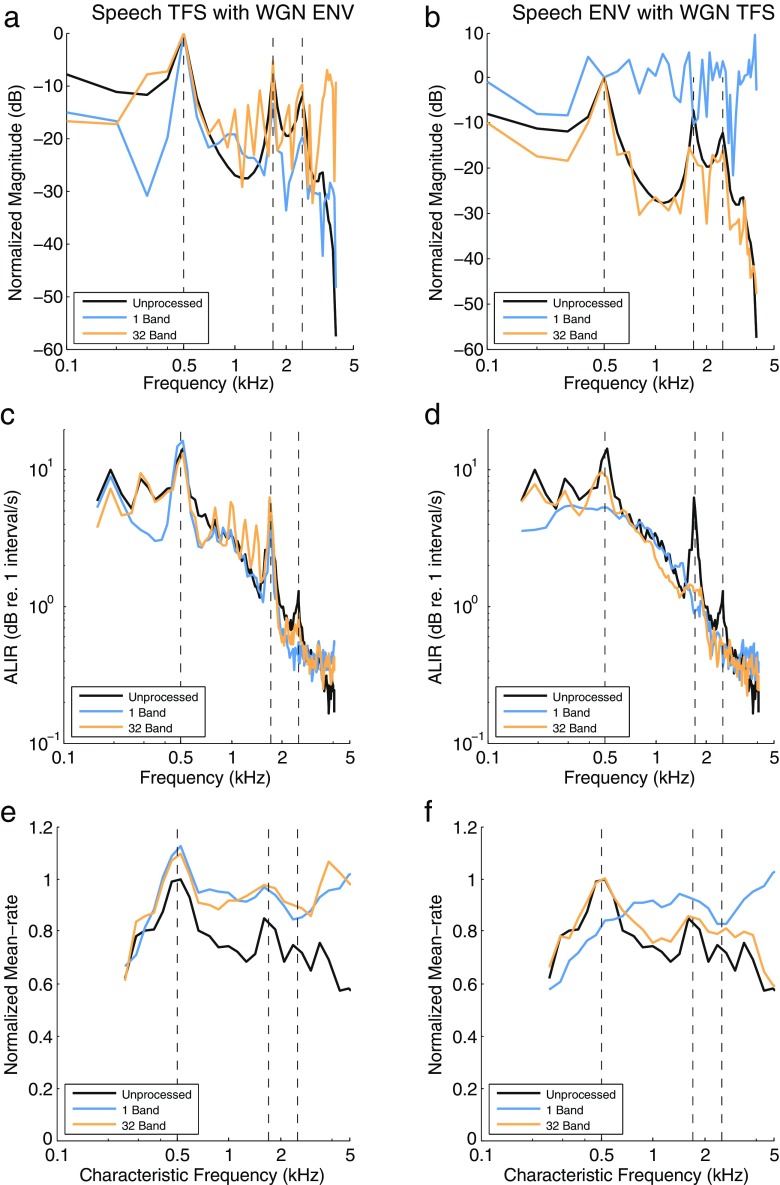
FIG. 8.
The effect of Speech TFS with WGN ENV (left column) and Speech ENV with WGN TFS (right column) vocoding on the acoustic (a, b) and neural (c–f) representations of the synthesized vowel /ε/. The vowel has a fundamental frequency of 100 Hz and five formant frequencies of 0.5, 1.7, 2.5, 3.3, and 3.7 kHz (see Miller et al. 1997). The frequencies of the first three formants are shown by the vertical dashed lines in all panels. a, b The spectral envelope for each chimaera type compared to the unprocessed vowel. c, d The average localized interval rate (ALIR) profiles, in units of decibels re. 1 interval per second, showing the degree of synchrony of AN fibers whose CFs are within 0.5 octave of each frequency sample in the stimulus. e, f The mean-rate discharge profiles as a function of CF for the time period of the unprocessed vowel.