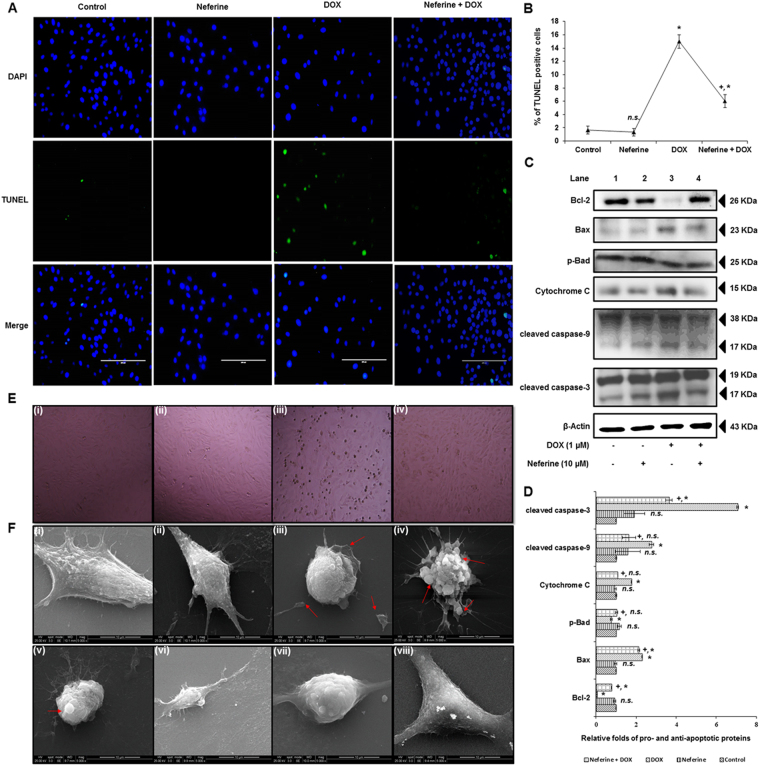
Figure 6.
Effect of neferine and DOX-treatment on DNA breaks, intrinsic apoptosis and morphological changes in H9c2 cells (A) Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) dUTP nick-end labeling showing reduced DNA breaks and apoptotic body formation by neferine pre-treatment. (B) % of TUNEL positive apoptotic nuclei. (C) Western blot analysis of neferine and DOX-treatment on pro- and anti-apoptotic protein levels. (D) Densitometry analysis of the protein bands of pro- and anti-apoptotic proteins. (E) Phase-contrast microscopic images of H9c2 cells. (i) Control cells. (ii) Neferine treated cells showing normal morphology. (iii) DOX-alone treated cells showing spindle shape shrinkage and detachment of cells from culture surface. (iv) Cells pre-treated with neferine followed by DOX-treatment reduced the shrinkage and rounding up of cells from the culture surface. (F) Morphological analysis of H9c2 cells by scanning electron microscopy. (i & ii) Control and neferine treatment showing the normal morphological architectures of elongated spindle shaped H9c2 cells with dense surface. (iii-v) DOX-treatment showing morphological changes like loss of spindle shape, cell shrinkage, rounding up of cells and membrane blebbing associated with apoptosis in H9c2 cells. (vi-viii) Neferine pre-treatment showing reduced structural abnormalities induced by DOX- treatment. The graphs represent mean ± s.d. of three individual experiments. *p < 0.05 significantly different from control, +p < 0.05 significantly different from DOX treated cells, n.s. = non-significantly different from control (one way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison).