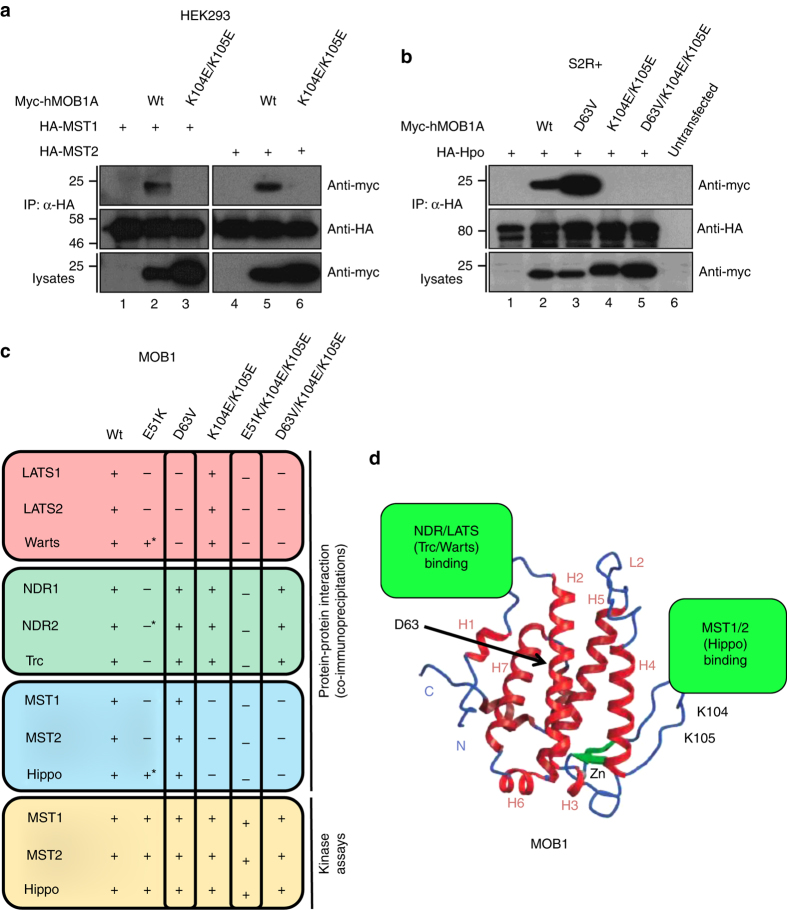
Fig. 3.
Definition of MOB1 variants with selective loss-of-interaction with Hippo core kinases. a Lysates of HEK293 cells expressing full-length HA-MST1 or HA-MST2 wild-type (wt) together with indicated full-length MOB1A versions were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) using anti-HA. Complexes were studied by immunoblotting using anti-myc (top) and anti-HA (middle). Input lysates were analyzed with anti-myc (bottom). The K104E/K105E mutations caused loss of binding to MST1/2. See Supplementary Fig. 19 for uncropped western blots. b Lysates of Drosophila S2R + cells expressing full-length HA-Hpo(wt) together with indicated full-length MOB1A versions were subjected to IP using anti-HA. Complexes were studied by immunoblotting using anti-myc (top) and anti-HA (middle). Input lysates were probed with anti-myc (bottom). Relative molecular weights are shown. See Supplementary Fig. 19 for uncropped western blots. c Schematic summary of the biochemical and molecular characterization of the indicated MOB1A variants presented in Supplementary Figs. 5–13. Noteworthy, NDR2 weakly interacted with MOB1(E51K), and Warts and Hpo bound normally to the E51K mutant as judged by co-immunoprecipitation experiments (marked by an asterisk), hence the E51K mutant was not studied further. d Model of human MOB1A(33–216) depicting the possibly opposing binding sites on MOB1 of NDR/LATS and MST1/2 kinases. Secondary structure elements of MOB1 are highlighted. The locations of Glu51, Asp63, and Lys104/Lys105 in MOB1 are indicated