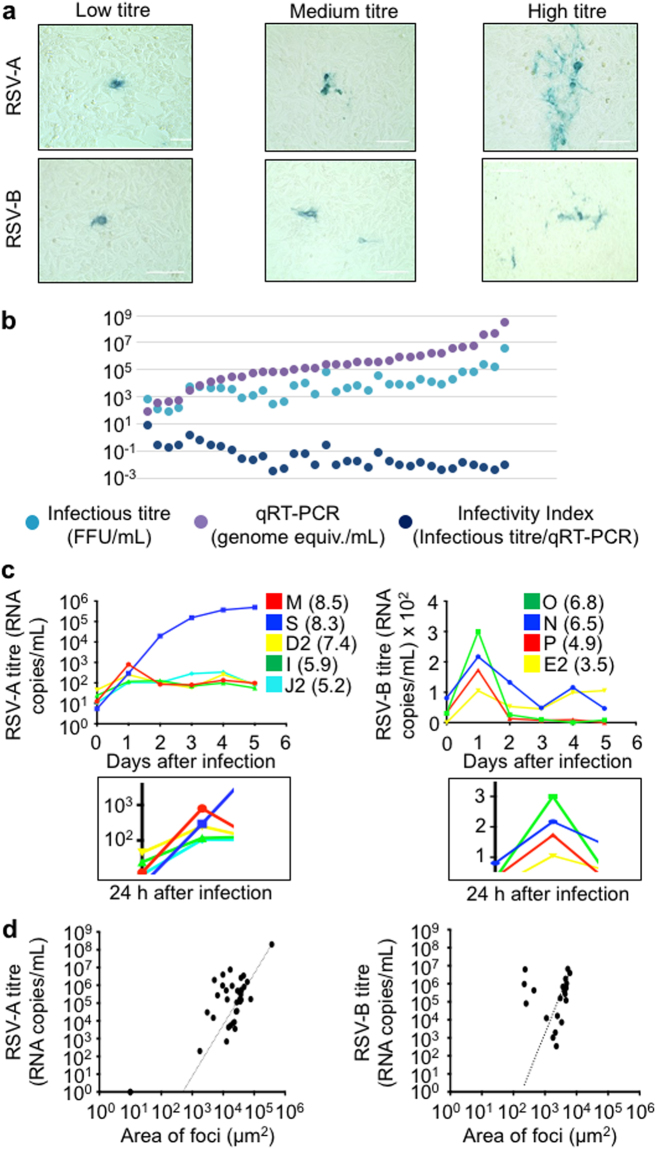
Figure 2.
Correlation of RSV isolate replication kinetics with patient sample titre. (a) Immortalized HEp-2 cells were inoculated with patient nasopharyngeal (NP) samples that were determined to be RSV type-A or type-B positive by the NxTAG RVP Luminex panel at PROVLab, Alberta, Canada. The HEp-2 cells were fixed and immunostained for RSV infection two days later. The morphology and size of the plaques were analyzed using automated color segmentation software on a digital phase contrast microscope. There was a range of sizes of foci of cell culture infection among the samples. (b) Comparison of RSV patient sample titres were determined by qRT-PCR and the number of focus forming units per mL. Infectivity index was determined by the dividing the infectious titre (FFU/mL) by the genome equivalents/mL (by qRT-PCR). (c) A replication time course over 5 days of RSV type-A and type-B isolates in immortalized cells. HEp-2 cells were inoculated by equal inputs of genomic equivalents as determined by qRT-PCR of two high titre, medium titre and low titre isolates of RSV type-A and RSV type-B to determine whether there was a difference in replication kinetics of isolates of different titres in patient samples. The number in parentheses beside the sample identifier indicates the RSV titre in the original patient’s sample. Inset below: viral titres 24 hrs post infection. (d), RSV type-A and B titres were determined by qRT-PCR and plotted versus the area of foci of infection after 48 hours on HEp-2 cells. A line of best fit is shown for RSV type-A and type-B.