FIGURE 6.
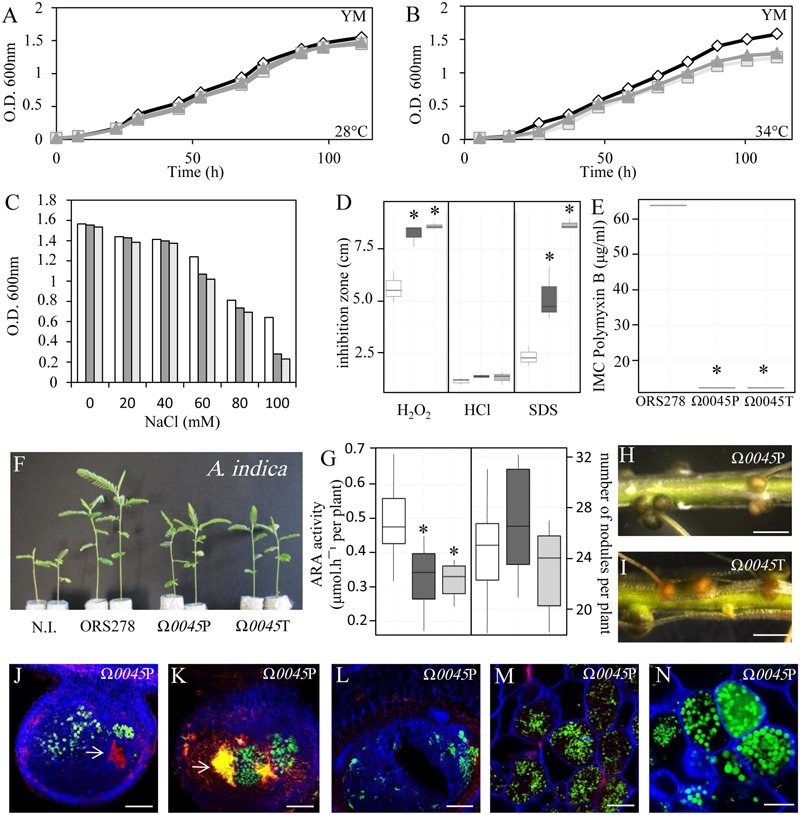
The BRADO0045 mutation affect both free-living and symbiotic states of ORS278. (A–F) Growth of ORS278 (white), Ω0045P (dark gray) and Ω0045T (gray) mutants in YM medium at 28°C (A) and 34°C (B) (n = 1). (C) NaCl resistance of ORS278 (white), Ω0045P (dark gray) and Ω0045T (gray) strains cultivated in rich medium (YM), at 34°C, n = 1. (D) Box plots representation of the Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), hydrogen chloride (HCl) and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) resistance of ORS278 (white), Ω0045P (dark gray) and Ω0045T (gray) mutants, as determined by disk diffusion assays using 5 μl of 5.5 M H2O2, 2N HCl or 10% of SDS (n = 9). (E) Box plots representation of the Polymyxin B resistance of ORS278 and the two Ω0045P and Ω0045T mutants, as determined by Etest (Etest®bioMérieux) on YM medium (n = 3); (F) Comparison of the growth of A. indica (aerial part), non-inoculated (N.I.) or inoculated with ORS278, Ω0045P or Ω0045T mutants. The experiment was carried out in duplicate with 10 plants per condition. (G) Box plots representation of the quantification of ARA and number of nodules per plant inoculated with ORS278 (white), Ω0045P (dark gray) or Ω0045T (gray) mutants in A. indica. Whole roots of A. indica inoculed with the Ω0045P mutant (H) or the Ω0045T mutant of ORS278 (I); scale bars: 2 mm. (J–N) Nodule thin sections of A. indica elicited by the Ω0045P mutant and viewed by confocal microscopy; scale bars: 300 μm (J–L) and 20 μm (M,N). (J,K) Whites arrows indicate plant defense reactions. (D,E,G) ∗P < 0.01, by Tukey’s honestly significant difference test.
