Figure 2.
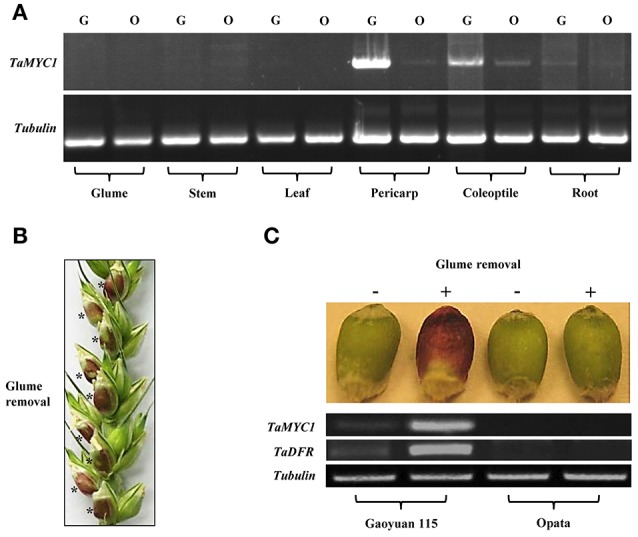
Transcriptional characteristics of TaMYC1. (A) Relative transcript levels of TaMYC1 in the different organs/tissues (glume, stem, leaf, pericarp, coleoptile, and root) of Gaoyuan 115 (G) and Opata (O) as assessed using semi-quantitative RT-PCR. The amplification of wheat tubulin gene served as an internal control. (B) Artificial removal of outer and inner glumes induced purple AP accumulation in the developing grains of Gaoyuan 115. Glume removal was conducted at 14 days after flowering, with AP induction becoming visible in the grains (indicated by asterisks) 2 days after the treatment. (C) Relative transcript levels of TaMYC1 and TaDFR in the grains of Gaoyuan 115 and Opata without (−) or with (+) glume removal treatment. The transcript levels were evaluated using semi-quantitative RT-PCR with the amplification of wheat tubulin gene as an internal control. The data displayed are representative of three separate tests.
