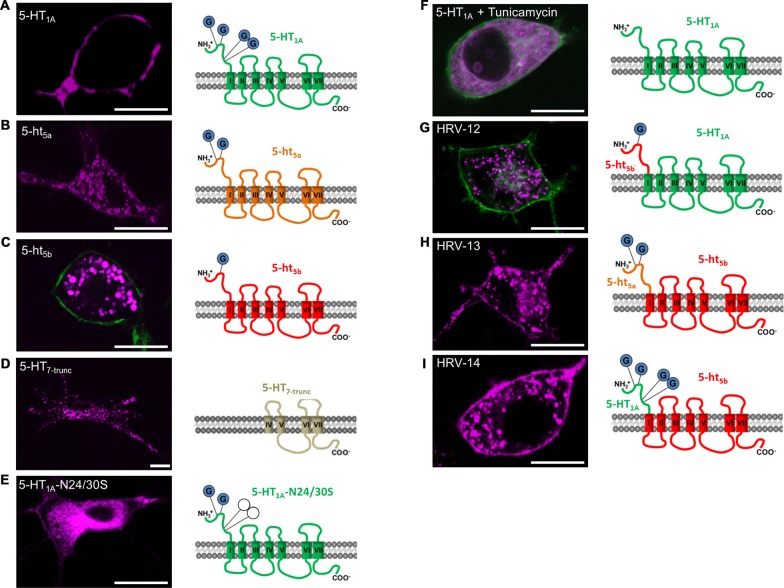
Figure 2.
Effect of N-terminal glycosylation on membrane trafficking of 5-HT receptors. For all experiments, N1E-115 cells were transiently transfected with the same amount of receptor corresponding deoxyribonucleic acid (cDNA). All receptor constructs are shown in purple. If the outline of the cell was not easily recognized, a membrane label (GAP-43) was co-transfected (green). (A) 5-HT1A possesses four glycosylation sites on the N-terminus and displays specific membrane localization. (B) 5-ht5a possesses only two glycosylation sites. In comparison to the other 5-HT receptors, 5-ht5a shows weak membrane staining, but pronounced staining of endosomal compartments. (C) 5-ht5b possesses only one glycosylation site and membrane localization of the receptor is not detectable. (D) Artificially truncated 5-HT receptor 5-HT7 (5-HT7-trunc) comprises the trans-membrane domains (TMDs) IV to VII and shows strong intracellular clustering with no discernable membrane staining. (E) Site-directed mutagenesis of Asparagine (N) to Serine (S) at positions 24 and 30 in 5-HT1A-N24/30S removes two of four glycosylation sites and greatly reduces membrane trafficking of the mutated receptor. (F) Tunicamycin blocks the formation of protein N-glycosidic linkages by inhibiting the transfer of N-acetylglycosamine-1-phosphate to dilichol mono-phosphate. Application of Tunicamycin (1 μg/ml) to cells expressing 5-HT1A removes the receptor from the cell membrane. (G) Replacing the N-terminal domain of 5-HT1A containing 4 glycosylation sites with the N-terminal domain of 5-ht5b with 1 glycosylation site completely abolishes membrane localization of the hybrid receptor and produces a clustered intracellular staining. (H) Replacing the N-terminal domain of 5-ht5b containing 1 glycosylation site with the N-terminal domain of 5-ht5a with 2 glycosylation sites produces a clustered intracellular staining and produces moderate membrane localization. (I) Replacing the N-terminal domain of 5-ht5b containing 1 glycosylation site with the N-terminal domain of 5-HT1A with 4 glycosylation sites does not prevent intracellular localization, but leads to significant membrane localization of the hybrid receptor. Scale bars in all images are 10 μm.