Fig. 2.
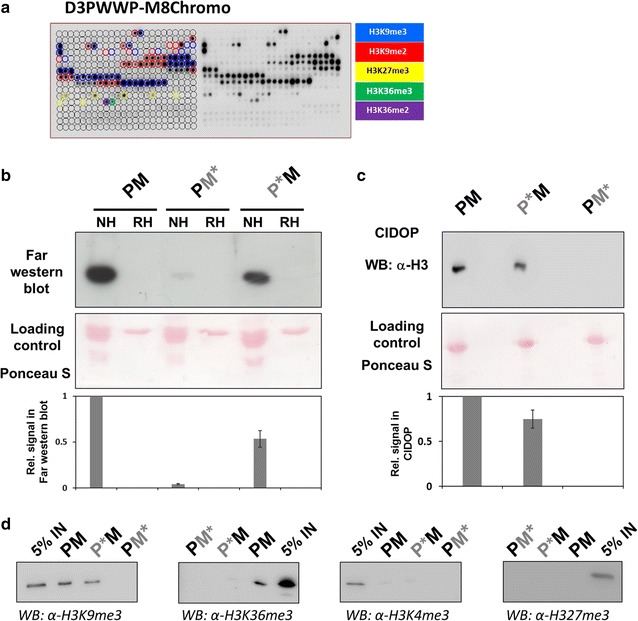
The D3PWWP-M8Chromo double reading domain specifically interacts with native histones and nucleosomes. a Peptide array specificity profiling of the hybrid D3PWWP-M8Chromo recombinant protein. The peptide spots are annotated on the left side of the array, and the color code denotes the presence of the designated histone PTM in different combinations. The D3PWWP-M8Chromo domain displayed binding to H3K9me3, H3K27me3, H3K36me2 and H3K36me3 containing peptides. See also Additional file 1: Figure S2A and Additional file 2: Table S6. b Far-western blot analyses with D3PWWP-M8Chromo (PM) and its variants containing mutations in the M8Chromo (PM*) or D3PWWP (P*M) domains with native histones (NH) and recombinant histones (RH). The bar diagram shows a quantification of the data based on two repetitions. Error bars indicate the SEM. c Precipitation of mononucleosomes with D3PWWP-M8Chromo WT and its variants under stringent (CIDOP) washing conditions and detection with anti-H3 antibody. The Ponceau S staining represents a loading control of D3PWWP-M8Chromo and its variants. The bar diagram shows a quantification of the data based on two repetitions. Error bars indicate the SEM. See also Additional file 1: Figure S2B and C. d Specificity of the mononucleosomal CIDOP with D3PWWP-M8Chromo (PM) and its variants containing mutations in the M8Chromo (PM*) or D3PWWP (P*M) domains analyzed by western blot with the H3K9me3, H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 antibodies. 5% IN—5% input. See also Additional file 1: Figure S2
