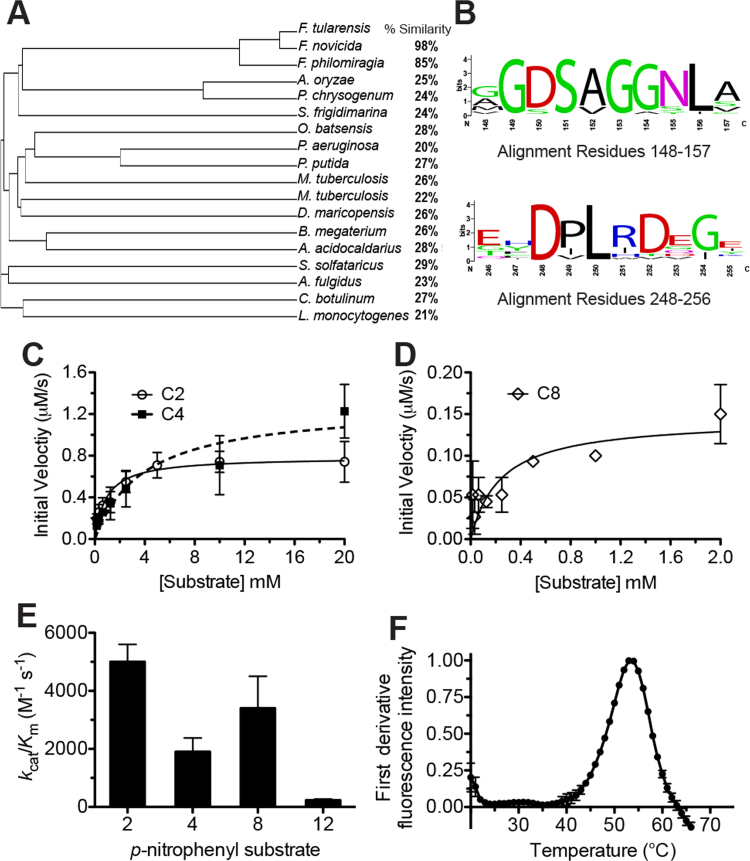
Fig. 1.
Biochemical characterization of FTT0941c. (A) Phylogenetic relationship between FTT0941c and homologous bacterial hydrolases. The amino acid sequence of FTT0941c was aligned with the 17 other bacterial hydrolases and a cladogram of the aligned proteins was constructed with percent similarities from Clustal Omega. Detailed sequence analysis is given in Supplementary Table 1. (B) Sequence conservation of residues adjacent to the proposed catalytic triad. Relative weightings and motif analysis performed using Weblogo [41]. Detailed sequence analysis given in Supplementary Table 1. (C) and (D) Kinetic activity of FTT0941c against p-nitrophenyl acetate (C2), p-nitrophenyl butyrate (C4), and p-nitrophenyl octanoate (C8). The kinetic activity of FTT0941c for C2 and C4 was measured from 20 mM to 156 μM and for C8 from 2 mM to 15.6 μM to account for its lower Km value and solubility. Data points were fitted to the Michaelis-Menten equation and are shown ±SE. Values for kinetic constants are given in Table 1. (E) Catalytic efficiency of FTT0941c against p-nitrophenyl substrates (p-nitrophenyl acetate (2), p-nitrophenyl butyrate (4), p-nitrophenyl octanoate (8), and p-nitrophenyl laurate (12)). Catalytic efficiency values (kcat/Km) are given ±SE. Detailed kinetic values are given in Table 1. (F) Thermal stability of FTT0941c. The folded to unfolded transition for wild-type FTT0941c (0.3 mg/mL in PBS) was observed by DSF. The measurement was completed in triplicate and is shown ±SE.