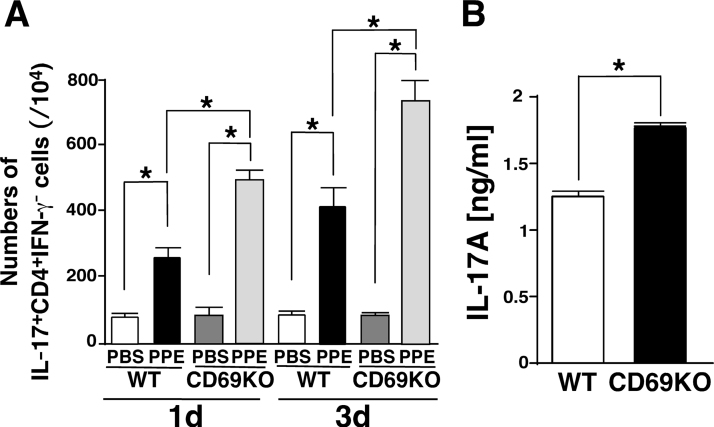
Fig. 4.
IL-17-producing activity of Th17 and γδT cells from WT and CD69KO mice. A) The PPE-increased and CD69-deficinecy-sensitive Th17 differentiation. Single cell suspensions of LNCs from PPE-instilled WT and CD69KO mice at 1 and 3 dpi were stimulated with PMA+ionomycin or PBS for 3 h and subjected to surface staining for CD4 and intracellular staining for IL-17 and IFN-γ. Quantification of IL-17+CD4+IFN-γ− T cells was performed with FlowJo software. Data are shown as mean±S.E.M. (n=4–6). *P<0.05, significantly different from value of WT-PBS group (ANOVA followed by Tukey's test). B) IL-17 production in γδ T cells from the two genotypes. TCRγδ+ cells were prepared from the lymph nodes of naïve WT and CD69KO mice and stimulated with IL-1β+IL-23. The resulting supernatants were subjected to ELISA for mouse IL-17A. We confirmed that IL-17A levels in the supernatants from unstimulated γδ T cells of the two genotypes were below the detection limit. Data are shown as mean±S.E.M. (n=6). *P<0.05, significantly different from value of WT group by Student's t test.