Figure 2. CDRH2 germline encoded and somatically mutated residues of CAP256.09 and CAP256.25 Abs are important in sialic acid recognition on glycan arrays.
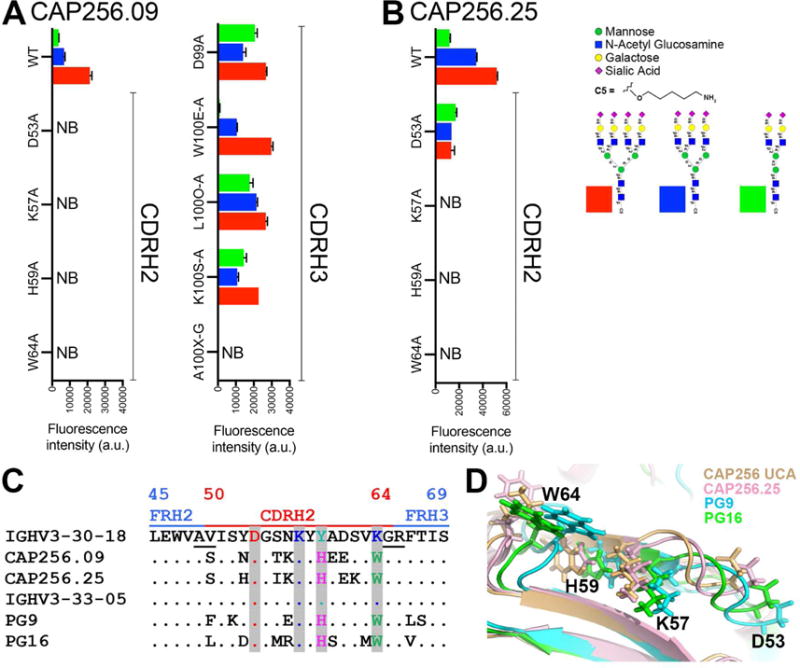
A. Reactivity on glycan microarrays of CAP256.09 wild type (WT) antibody and 9 variants. The 9 amino acid substitutions in the CAP256.09 heavy chain variable region include 4 in CDRH2 and 5 in CDRH3. B. Binding of CAP256.25 WT, CDRH2 Ab variants to glycan on the glycan microarray. C. Amino acid sequence alignment of the CDRH2 and parts of the FRH2 and FRH3 region of CAP256.09 and PG9 V2 apex bnAb prototypes with their respective germline VH-genes. Kabat numbering is indicated. The alignment shows that both V2 apex bnAb prototypes retain the germline-encoded residues at CDRH2 positions D53 and K57 and accumulate two common somatic mutations (Y59H and K64W). D. Structural alignment of CAP256 UCA (wheat), CAP256.25 (light pink), PG9 (cyan) and PG16 (green) bnAbs highlighting 4 amino acid positions in the CDRH2 region with side chains as sticks. See also Figure S3
