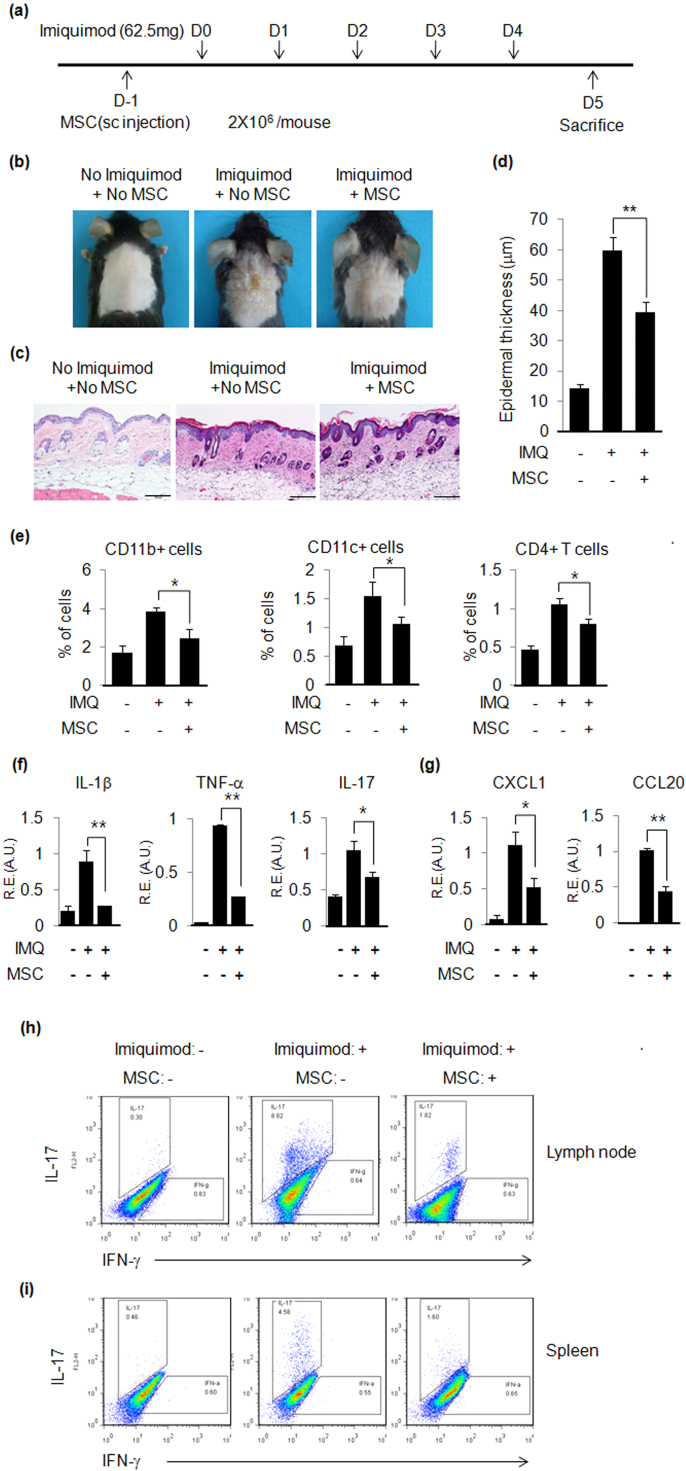
Fig. 3.
hUCB-MSCs inhibit imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice. (a) Experimental scheme for imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation and hUCB-MSC treatment. (b) Picture of imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice. hUCB-MSCs ameliorated imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation. (c) H&E staining of mouse back skin. Bar=100 µm (d) Epidermal thickness was increased by imiquimod and subcutaneous injection of hUCB-MSCs reduced the increased epidermal thickness. Epidermal thickness was measured at several regions throughout the skin section. (e) Percentages of immune cells in the skin. (f) Psoriasis-related pro-inflammatory cytokine and (g) chemokine gene expression was determined by real-time PCR. R.E: Relative Expression. A.U.: Arbitrary Unit. Intracellular staining of (h) lymph node cells and (i) spleen cells was performed as described in Materials and Methods section. Data are shown as mean±SEM. *P<0.05, **P<0.005.