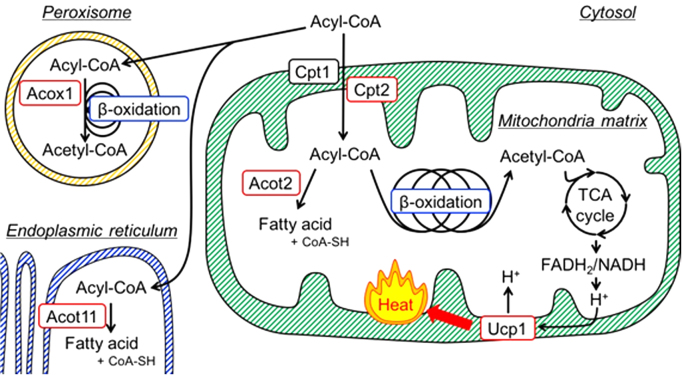
Fig. 4.
In brown adipocytes, acyl-CoA is transported via Cpt (Cpt1 and Cpt2) to the mitochondria matrix. Acot2 is induced along with β-oxidation enzymes and hydrolyzed some of acyl-CoA to generate fatty acid and CoA-SH. Thus, upregulation of Acot2 serves to maintain an adequate rate of β-oxidation by modulating the substrate supply and retaining the level of coenzymes used in the TCA cycle and β-oxidation itself. Ucp1 releases the energy extracted from fatty acids via β-oxidation followed by TCA cycle as heat (i.e. fatty acid combustion) by uncoupling ETC from the oxidative phosphorylation. These proteins (Cpt2, Acot2 and Ucp1) contribute to efficient oxidation of fatty acids in mitochondria. Acox1 oxidizes fatty acid to promote β-oxidation in peroxisome. Acot11 hydrolyzes some acyl-CoA to fatty acid and CoA-SH in the endoplasmic reticulum. Acot, acyl-CoA thioesterase; Acox1, acyl-CoA oxidase; Cpt, carnitine palmitoyltransferase; ETC, electron transport chain; TCA, tricarboxylic acid; Ucp, uncoupling protein.