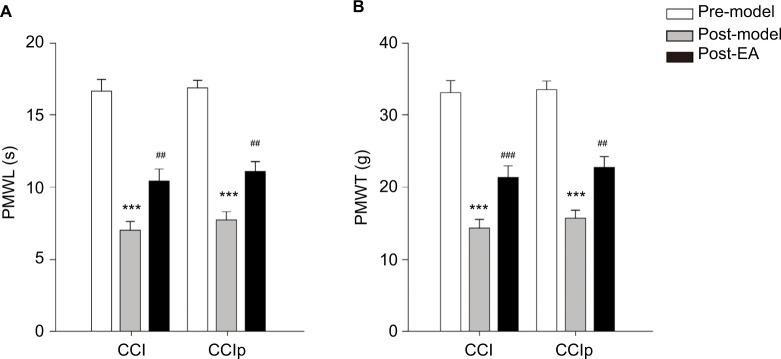
Figure 3.
Effect of EA at GB30 on PMWL and PMWT in CCI and CCIp rats.
Notes: (A) In either CCI (n=7) or CCIp (n=10) rats, PMWL was decreased significantly on day 5 after nerve ligation (post-model) compared to 1 day before nerve ligation (pre-model) (***P<0.001, paired t-test). No significant difference was found between CCI and CCIp rats (unpaired t-test). EA at GB30 caused significant increase in PMWL compared to post-model (##P<0.01, paired t-test); however, no significant difference was found between groups after EA at GB30 (unpaired t-test). (B) PMWT was significantly reduced after nerve ligation compared to one day before nerve ligation in CCI and CCIp rats (***P<0.001, paired t-test). There was no significant difference between CCI and CCIp rats (unpaired t-test). EA at GB30 significantly augmented PMWT in both CCI (###P<0.001, unpaired t-test) and CCIp rats (##P<0.01, paired t-test) compared to post-model, and there was no significant difference between both groups after EA at GB30 (unpaired t-test).
Abbreviations: CCI, chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve; CCIp, chronic constriction injury of the partial sciatic nerve; EA, electroacupuncture; PMWL, paw mechanical withdrawal latency; PMWT, paw mechanical withdrawal threshold.