Figure 5. Glia direct pioneer and follower-axon guidance using distinct signaling pathways.
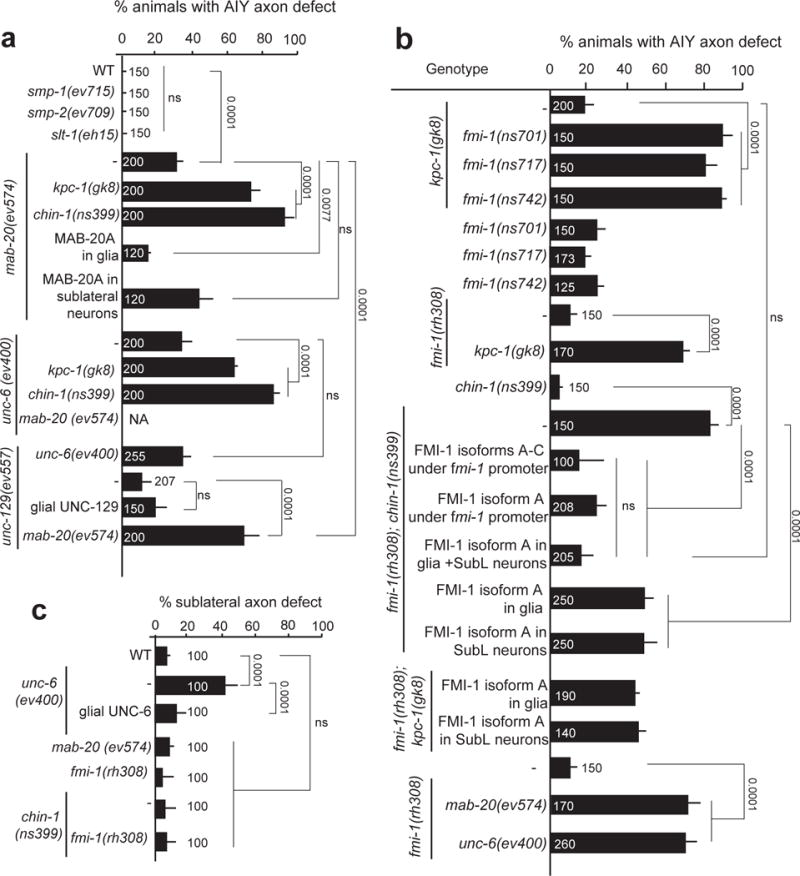
(a, c) UNC-6/Netrin and MAB-20/Semaphorin regulate nerve-ring assembly. UNC-6 guides primarily pioneer SubL axons while MAB-20 specifically guides follower axons and both act from glia. (b,c) FMI-1/Flamingo/CELSR can act cooperatively from SubL commissure neurons and glia to drive nerve-ring assembly, by specifically guiding follower axons. (a–c) cDNA expression of MAB, 20, UNC-6 and FMI-1 is driven by Pmir-228 (glia), Pceh-17 or Pceh-24 (SubL neurons), or endogenous regulatory regions. Expression patterns are described in Supplementary Methods and Supplementary Tables S8, S10. Numbers inside bars: total animals scored per genotype, n=4 independent scoring experiments or number of transgenic lines in rescue experiments. Mean +/− Error bars: SEM. Numbers above bars, p values from Fisher’s exact test. ns: non significant.
