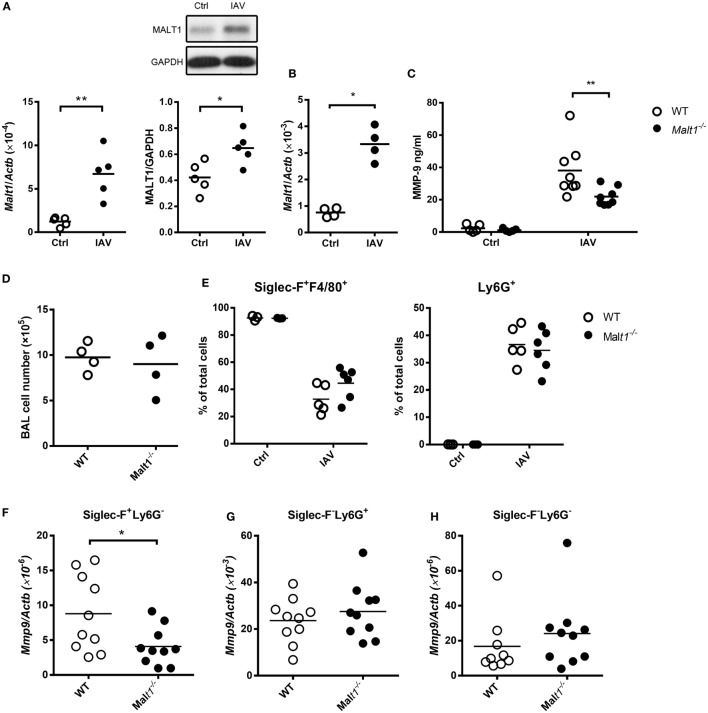
Figure 6.
Influenza A virus infection induces mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1 (MALT1) upregulation that contributes to matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) production in the lungs. (A) Wild-type mice were infected with of 5 × 104 PFU of WSN virus intratracheally. Lungs were harvested from uninfected and infected mice on day 2 after infection. Total RNA in lungs were extracted and applied to qPCR. The mRNA levels of Malt1was normalized against Actb (left panel). Lysates were blotted with anti-MALT1 and anti-GAPDH antibodies (upper right panel) and the intensity of MALT1 was normalized against that of GAPDH (lower right panel). One representative experiment is shown. (B–H) Malt1−/− and/or wild-type mice were infected with 5 × 103 PFU of WSN virus intratracheally. (B,D) On day 4 after infection, bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cells were (B) subject to RNA extraction for the determination of the levels of Malt1 transcripts by qPCR and (D) counted for the number of cells. (C,E–H) BAL was collected on day 2 after infection. (C) The concentration of MMP-9 in BAL was quantified by ELISA. (E) Cells in BAL were stained with anti-Siglec-F, anti-F4/80, and anti-Ly6G antibodies. Cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. (F–H) Cells in BAL were sorted by their expressions of Siglec-F and Ly6G surface markers. Total RNA of sorted cells were extracted and Mmp9 mRNA were quantified by qPCR and normalized against Actb. Each dot represents cells from one mouse. Data are a compilation of two (A,B,D) and three (C,E–H) independent experiments. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 compared to control. Data in (A,B,D,F–H) were analyzed by Mann–Whitney U-test. Data in (C,E) were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s post hoc test.