Fig. 6.
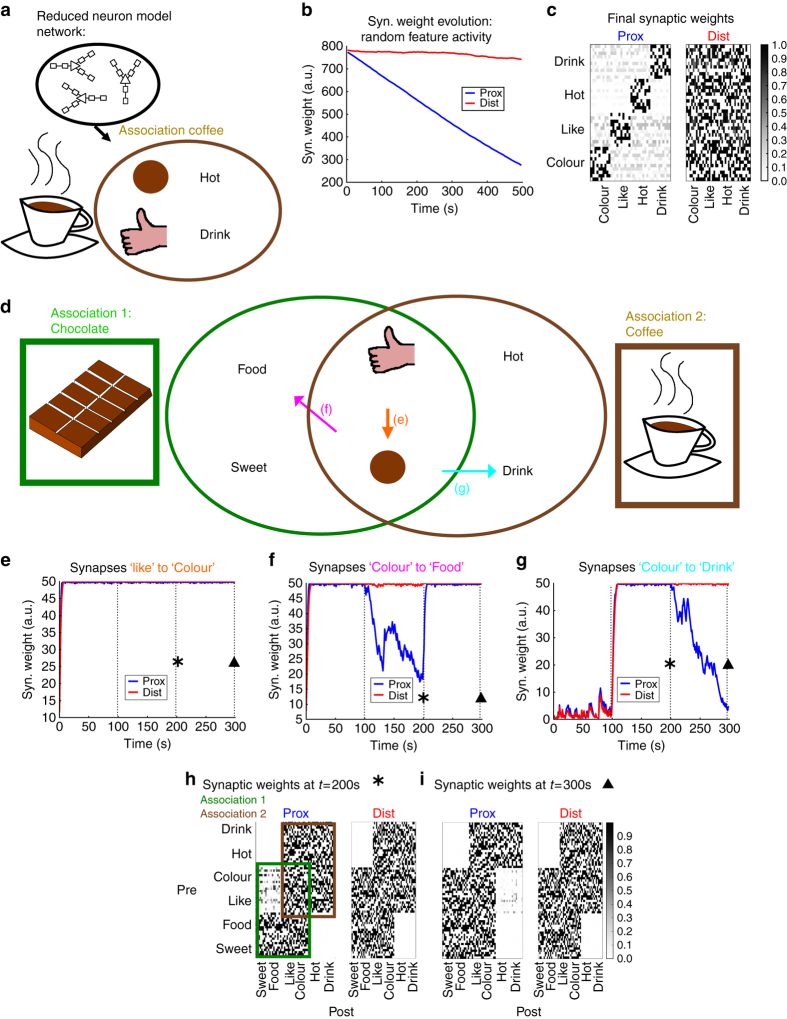
In networks, dLTP can protect previously learnt connections. a Top: A neuron model with simplified dendrites is implemented for the network simulations. The model consists of two compartments per dendrite, one representing a proximal compartment and one representing a distal compartment (see also Supplementary Fig. 5). Bottom: A network represents an associative memory (“coffee”), containing four subgroups of neurons which we will call “features”, in this case they are colour (brown), something you like, hot and drink. The initial weights are all-to-all and initiated at the maximum bound. b When randomly activating the individual features, the distal synaptic clusters are always activated together and evoke NMDA spikes. While proximal weights between features depress, distal weights remain close to the initial value. c The final synaptic weight matrix corresponding to panel b. d A second network consists of two associative memories, “chocolate” and “coffee”. Each association is composed of four features. The associations share two features (“Colour” and “Like”), the connectivity is all-to-all and all weights are initialised at the lower bound. e–g During the first 100 s, the “chocolate” association is activated ten times more frequently than the “coffee” association. Proximal and distal synaptic weights between neurons of the “chocolate” association are strengthened e, f. From 100 to 200 s, we reverse the activation probability: the “coffee” association is presented ten times more frequently. The synaptic weights between neurons of this association are now maintained or strengthened e, g. The proximal synapses towards features that are exclusively part of the “chocolate” association are now weakened, while the corresponding distal synapses remain more stable f. During the final 100 s, the same protocol as in the initial 100 s is followed, activating mostly “chocolate” association. The proximal synapses towards features that are exclusively part of the “coffee” association are now weakened, while the corresponding distal synapses remain more stable g. h, i Weight matrix after 200 s (h and asterisk in e–g) and 300 s (i and triangle in e–g) of the simulation. Notice the difference in the proximal weights (left panels) from features “Like” and “Colour” to features “Sweet”,”Food”,”Hot” and “Drink”. The distal weights (right panels) remain similar